齒
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual
[edit]| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
| Traditional | 齒 |
|---|---|
| Shinjitai | 歯 |
| Simplified | 齿 |
Han character
[edit]齒 (Kangxi radical 211, 齒+0, 15 strokes, cangjie input 卜一山人人 (YMUOO), four-corner 21772, composition ⿱止𠚕)
- Kangxi radical #211, ⿒.
- Shuowen Jiezi radical №38
Derived characters
[edit]Descendants
[edit]References
[edit]- Kangxi Dictionary: page 1532, character 8
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 48583
- Dae Jaweon: page 2070, character 5
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 7, page 4788, character 1
- Unihan data for U+9F52
Chinese
[edit]| trad. | 齒 | |
|---|---|---|
| simp. | 齿 | |
| alternative forms | ||
Glyph origin
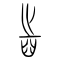
[edit]| Historical forms of the character 齒 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |

|
|

|

|
Pictogram (象形) – a mouth full of teeth. 之 (zhī) or 止 (zhǐ) was later added on top as a phonetic component.
Etymology
[edit]Unclear. Not related to Tibetan མཆེ་བ (mche ba, “fang, tusk”), which is cognate with 齻/𱌺 (diān, “eyetooth”), but may be the same word as Proto-Min *kʰiᴮ (“tooth”). Another possibility is a derivation from an Austroasiatic etymon; Schuessler, 2007 (p.188) suggests a possible relationship to Khmer ខ្នាយ (khnaay, “tusk, spur”), as Austroasiatic medial /n/ is often deleted in loans.
Pronunciation
[edit]- Mandarin
- (Standard)
- (Chengdu, Sichuanese Pinyin): ci3
- (Dungan, Cyrillic and Wiktionary): цы (cɨ, III)
- Cantonese (Jyutping): ci2
- Gan (Wiktionary): ci3
- Hakka
- Jin (Wiktionary): ci2
- Northern Min (KCR): chǐ
- Eastern Min (BUC): kī / chī
- Southern Min
- Wu (Shanghai, Wugniu): 5tshy
- Xiang (Changsha, Wiktionary): chr3
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Hanyu Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄔˇ
- Tongyong Pinyin: chǐh
- Wade–Giles: chʻih3
- Yale: chř
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: chyy
- Palladius: чи (či)
- Sinological IPA (key): /ʈ͡ʂʰʐ̩²¹⁴/
- (Chengdu)
- Sichuanese Pinyin: ci3
- Scuanxua Ladinxua Xin Wenz: c
- Sinological IPA (key): /t͡sʰz̩⁵³/
- (Dungan)
- Cyrillic and Wiktionary: цы (cɨ, III)
- Sinological IPA (key): /t͡sʰz̩⁴⁴/
- (Note: Dungan pronunciation is currently experimental and may be inaccurate.)
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Jyutping: ci2
- Yale: chí
- Cantonese Pinyin: tsi2
- Guangdong Romanization: qi2
- Sinological IPA (key): /t͡sʰiː³⁵/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Gan
- (Nanchang)
- Wiktionary: ci3
- Sinological IPA (key): /t͡sʰz̩²¹³/
- (Nanchang)
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: chhṳ́
- Hakka Romanization System: ciiˋ
- Hagfa Pinyim: ci3
- Sinological IPA: /t͡sʰɨ³¹/
- (Meixian)
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Neipu)
- Jin
- (Taiyuan)+
- Wiktionary: ci2
- Sinological IPA (old-style): /t͡sʰz̩⁵³/
- (Taiyuan)+
- Northern Min
- (Jian'ou)
- Kienning Colloquial Romanized: chǐ
- Sinological IPA (key): /t͡sʰi²¹/
- (Jian'ou)
- Eastern Min
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: kī / chī
- Sinological IPA (key): /kʰi³³/, /t͡sʰi³³/
- (Fuzhou)
- kī - vernacular;
- chī - literary.
- Southern Min
- khí - vernacular;
- chhí - literary.
- (Teochew)
- Peng'im: ki2 / cin2
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī-like: khí / tshíⁿ
- Sinological IPA (key): /kʰi⁵²/, /t͡sʰĩ⁵²/
- ki2 - vernacular;
- cin2 - literary.
- Dialectal data
- Middle Chinese: tsyhiX
- Old Chinese
- (Baxter–Sagart): /*t-[k]ʰə(ŋ)ʔ/
- (Zhengzhang): /*kʰjɯʔ/
Definitions
[edit]齒
- (anatomy) tooth
- (figurative) tooth- or zigzag-like thing, such as a sawtooth, cogwheel, or fern
- (figurative) age (of a person or animal)
- to juxtapose; to put side by side
- to utter; to mention
- † to employ; to take in
- (dialectal) to touch; to be in contact with
- (Xiang) pay attention, to be concerned with
Synonyms
[edit]| Variety | Location | Words |
|---|---|---|
| Formal (Written Standard Chinese) | 理, 管, 睬, 理睬, 理會 | |
| Northeastern Mandarin | Beijing | 理, 搭理, 搭咯 |
| Taiwan | 理, 管 | |
| Singapore | 理, 管 | |
| Jilu Mandarin | Jinan | 理, 搭理 |
| Central Plains Mandarin | Xi'an | 招, 理 |
| Southwestern Mandarin | Chengdu | 理, 睬, 理視, 耳視, 張視 |
| Wuhan | 邇, 理, 睬 | |
| Guilin | 理 | |
| Jianghuai Mandarin | Yangzhou | 睬 |
| Hefei | 理, 睬 | |
| Cantonese | Guangzhou | 睬, 理, 騷 |
| Hong Kong | 睬, 理, 騷 | |
| Yangjiang | 理, 睬 | |
| Singapore (Guangfu) | 理 | |
| Gan | Nanchang | 理, 搭 |
| Hakka | Meixian | 睬, 唰 |
| Jin | Taiyuan | 理, 理睬 |
| Northern Min | Jian'ou | 理 |
| Eastern Min | Fuzhou | 叕, 插 |
| Southern Min | Xiamen | 插, 插趖, 插潲, 插管, 管待, 嘀厾, 理落 |
| Quanzhou | 插, 插趖, 插潲, 嘀厾 | |
| Zhangzhou | 插, 插潲, 插管, 管待 | |
| Tainan | 插, 管, 管待 | |
| Penang (Hokkien) | 插潲 | |
| Singapore (Hokkien) | 插, 插潲, 管, 插管, 甩 | |
| Manila (Hokkien) | 插, 插潲, 管 | |
| Chaozhou | 睬 | |
| Shantou | 理 | |
| Jieyang | 睬 | |
| Singapore (Teochew) | 插 | |
| Zhongshan Min | Zhongshan (Longdu, Shaxi) | 理 |
| Wu | Shanghai | 睬, 理 rare |
| Suzhou | 理, 睬 | |
| Wenzhou | 朝, 理 | |
| Xiang | Changsha | 齒 |
| Shuangfeng | 齒, 搭, 邇 | |
Compounds
[edit]- 不以人齒/不以人齿
- 不好啟齒/不好启齿
- 不置齒頰/不置齿颊
- 不足掛齒/不足挂齿 (bùzúguàchǐ)
- 不足齒/不足齿
- 不足齒及/不足齿及
- 不足齒數/不足齿数
- 不齒/不齿 (bùchǐ)
- 乳齒/乳齿 (rǔchǐ)
- 令人不齒/令人不齿
- 令人切齒/令人切齿
- 令人齒冷/令人齿冷
- 伶牙俐齒/伶牙俐齿
- 何足掛齒/何足挂齿 (hézú guàchǐ)
- 俐齒伶牙/俐齿伶牙
- 借齒牙/借齿牙
- 兒齒/儿齿
- 共為脣齒/共为唇齿
- 共相脣齒/共相唇齿
- 分班序齒/分班序齿
- 切齒/切齿 (qièchǐ)
- 切齒咬牙/切齿咬牙
- 切齒拊心/切齿拊心
- 切齒腐心/切齿腐心
- 利齒兒/利齿儿
- 刺齒/刺齿
- 剔齒纖/剔齿纤
- 劍齒虎/剑齿虎 (jiànchǐhǔ)
- 劍齒象/剑齿象
- 半齒音/半齿音
- 口齒/口齿 (kǒuchǐ)
- 口齒伶俐/口齿伶俐
- 口齒便給/口齿便给
- 叩齒/叩齿
- 含齒戴髮/含齿戴发
- 咬牙切齒/咬牙切齿 (yǎoyáqièchǐ)
- 噙齒戴髮/噙齿戴发
- 嚼齒/嚼齿
- 壯齒/壮齿
- 大臼齒/大臼齿 (dàjiùchǐ)
- 大齒輪/大齿轮
- 孺齒/孺齿
- 尊年尚齒/尊年尚齿
- 小臼齒/小臼齿 (xiǎojiùchǐ)
- 尚齒/尚齿
- 屐齒/屐齿
- 差速齒輪/差速齿轮
- 年齒/年齿 (niánchǐ)
- 幼齒/幼齿 (yòuchǐ)
- 序齒/序齿 (xùchǐ)
- 怒目切齒/怒目切齿
- 恆齒/恒齿 (héngchǐ)
- 戴髮含齒/戴发含齿
- 投梭折齒/投梭折齿
- 拊膺切齒/拊膺切齿
- 挂齒
- 捕蛇去齒/捕蛇去齿
- 掛齒/挂齿 (guàchǐ)
- 搜根剔齒/搜根剔齿
- 撇齒拉嘴/撇齿拉嘴
- 攘袂切齒/攘袂切齿
- 啟齒/启齿 (qǐchǐ)
- 斑狀齒/斑状齿
- 明眸皓齒/明眸皓齿
- 星眸皓齒/星眸皓齿
- 智齒/智齿 (zhìchǐ)
- 暮齒/暮齿
- 有齒郵票/有齿邮票
- 朱口皓齒/朱口皓齿
- 朱脣榴齒/朱唇榴齿
- 朱脣皓齒/朱唇皓齿
- 歷齒/历齿
- 毀齒/毁齿
- 永久齒/永久齿
- 沒齒/没齿
- 沒齒不忘/没齿不忘
- 沒齒難忘/没齿难忘 (mòchǐnánwàng)
- 沒齒難泯/没齿难泯
- 涅齒/涅齿
- 混合齒列/混合齿列
- 潔齒劑/洁齿剂
- 無足掛齒/无足挂齿 (wúzúguàchǐ)
- 無齒郵票/无齿邮票
- 牙齒/牙齿 (yáchǐ)
- 犬馬齒殲/犬马齿歼
- 犬馬齒窮/犬马齿穷
- 犬馬齒索/犬马齿索
- 犬齒/犬齿 (quǎnchǐ)
- 生齒/生齿 (shēngchǐ)
- 生齒日繁/生齿日繁 (shēngchǐrìfán)
- 當門牙齒/当门牙齿
- 痛心切齒/痛心切齿
- 發皓齒/发皓齿
- 發脫口齒/发脱口齿
- 皓齒/皓齿 (hàochǐ)
- 皓齒明眸/皓齿明眸
- 皓齒星眸/皓齿星眸
- 皓齒朱脣/皓齿朱唇
- 皓齒蛾眉/皓齿蛾眉
- 眷齒/眷齿
- 瞋目切齒/瞋目切齿
- 禍發齒牙/祸发齿牙
- 科牙磕齒/科牙磕齿
- 稚齒/稚齿
- 種植義齒/种植义齿
- 羊齒/羊齿
- 義齒/义齿 (yìchǐ)
- 脣不遮齒/唇不遮齿
- 脣亡齒寒/唇亡齿寒 (chúnwángchǐhán)
- 脣紅齒白/唇红齿白
- 脣腐齒落/唇腐齿落
- 脣齒/唇齿 (chúnchǐ)
- 脣齒之邦/唇齿之邦
- 脣齒相依/唇齿相依 (chúnchǐxiāngyī)
- 脣齒音/唇齿音 (chúnchǐyīn)
- 臼齒/臼齿 (jiùchǐ)
- 舌齒音/舌齿音
- 蛾眉皓齒/蛾眉皓齿
- 裂眥嚼齒/裂眦嚼齿
- 見齒/见齿
- 象齒焚身/象齿焚身
- 資淺齒少/资浅齿少
- 輔車脣齒/辅车唇齿
- 輥齒輪/辊齿轮
- 連齒木屐/连齿木屐
- 鄉黨尚齒/乡党尚齿
- 釘齒耙/钉齿耙 (dīngchǐpá)
- 鋸齒/锯齿 (jùchǐ)
- 鋸齒草/锯齿草
- 鐵齒/铁齿 (tiěchǐ)
- 門齒/门齿 (ménchǐ)
- 阻生齒/阻生齿
- 雁齒/雁齿
- 雌牙扮齒/雌牙扮齿
- 雍齒封侯
- 韶顏稚齒/韶颜稚齿
- 頭童齒豁/头童齿豁
- 馬齒/马齿
- 馬齒加長/马齿加长
- 馬齒徒增/马齿徒增
- 馬齒徒長/马齿徒长
- 馬齒莧/马齿苋 (mǎchǐxiàn)
- 馬齒豆/马齿豆 (mǎchǐdòu)
- 馬齒長/马齿长
- 駒齒未落/驹齿未落
- 鬥口齒/斗口齿
- 鬥牙拌齒/斗牙拌齿
- 鬥牙鬥齒/斗牙斗齿
- 黃髮兒齒/黄发儿齿 (huángfà'érchǐ)
- 鼻偃齒露/鼻偃齿露
- 齊齒/齐齿
- 齊齒呼/齐齿呼 (qíchǐhū)
- 齒亡舌存/齿亡舌存
- 齒冠/齿冠 (chǐguān)
- 齒冷/齿冷 (chǐlěng)
- 齒列/齿列
- 齒劍/齿剑 (chǐjiàn)
- 齒危髮秀/齿危发秀
- 齒及/齿及 (chǐjí)
- 齒吻/齿吻
- 齒如含貝/齿如含贝
- 齒如齊貝/齿如齐贝
- 齒尊/齿尊
- 齒弊舌存/齿弊舌存
- 齒式/齿式
- 齒德俱增/齿德俱增
- 齒擊/齿击
- 齒杖/齿杖
- 齒根/齿根 (chǐgēn)
- 齒條/齿条 (chǐtiáo)
- 齒槽/齿槽
- 齒次/齿次
- 齒決/齿决
- 齒牙/齿牙
- 齒牙為猾/齿牙为猾
- 齒牙為禍/齿牙为祸
- 齒牙餘論/齿牙余论
- 齒痛/齿痛 (chǐtòng)
- 齒白脣紅/齿白唇红
- 齒石/齿石
- 齒縫/齿缝
- 齒耙/齿耙
- 齒舌/齿舌
- 齒若編貝/齿若编贝
- 齒落舌鈍/齿落舌钝
- 齒落髮白/齿落发白
- 齒讓/齿让
- 齒豁頭童/齿豁头童
- 齒質/齿质
- 齒輪/齿轮 (chǐlún)
- 齒遇/齿遇
- 齒錄/齿录
- 齒音/齿音 (chǐyīn)
- 齒頰生香/齿颊生香
- 齒頰留香/齿颊留香
- 齒髓/齿髓
- 齒髓腔/齿髓腔
- 齒髮/齿发 (chǐfà)
- 齒鯨/齿鲸 (chǐjīng)
- 齒齒/齿齿
- 齒齦/齿龈 (chǐyín)
- 齒齲/齿龋 (chǐqǔ)
- 齠年稚齒/龆年稚齿
- 齧齒目/啮齿目 (nièchǐmù)
- 齯齒/𫠜齿
- 齲齒/龋齿 (qǔchǐ)
- 齲齒笑/龋齿笑
References
[edit]- “齒”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database)[1], 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
Japanese
[edit]| 歯 | |
| 齒 |
Kanji
[edit](Hyōgai kanji, kyūjitai kanji, shinjitai form 歯)
Readings
[edit]Korean
[edit]Etymology
[edit]From Middle Chinese 齒 (MC tsyhiX). Recorded as Middle Korean 치〯 (chǐ) (Yale: chi) in Hunmong Jahoe (訓蒙字會 / 훈몽자회), 1527.
Hanja
[edit]Compounds
[edit]References
[edit]- 국제퇴계학회 대구경북지부 (國際退溪學會 大邱慶北支部) (2007). Digital Hanja Dictionary, 전자사전/電子字典. [2]
Vietnamese
[edit]Han character
[edit]齒: Hán Việt readings: xỉ (
齒: Nôm readings: xỉ[1][2][4], xỉa[1][3][5], xẻ[3]
References
[edit]- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Kangxi Radicals block
- CJKV characters simplified differently in Japan and China
- Han character radicals
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- Shuowen radicals
- Han pictograms
- Mandarin terms with audio pronunciation
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Sichuanese lemmas
- Dungan lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Gan lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Jin lemmas
- Northern Min lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Xiang lemmas
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese hanzi
- Mandarin hanzi
- Sichuanese hanzi
- Dungan hanzi
- Cantonese hanzi
- Gan hanzi
- Hakka hanzi
- Jin hanzi
- Northern Min hanzi
- Eastern Min hanzi
- Hokkien hanzi
- Teochew hanzi
- Wu hanzi
- Xiang hanzi
- Middle Chinese hanzi
- Old Chinese hanzi
- Chinese nouns
- Mandarin nouns
- Sichuanese nouns
- Dungan nouns
- Cantonese nouns
- Gan nouns
- Hakka nouns
- Jin nouns
- Northern Min nouns
- Eastern Min nouns
- Hokkien nouns
- Teochew nouns
- Wu nouns
- Xiang nouns
- Middle Chinese nouns
- Old Chinese nouns
- Chinese verbs
- Mandarin verbs
- Sichuanese verbs
- Dungan verbs
- Cantonese verbs
- Gan verbs
- Hakka verbs
- Jin verbs
- Northern Min verbs
- Eastern Min verbs
- Hokkien verbs
- Teochew verbs
- Wu verbs
- Xiang verbs
- Middle Chinese verbs
- Old Chinese verbs
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese terms spelled with 齒
- zh:Anatomy
- Mandarin terms with usage examples
- Chinese terms with obsolete senses
- Chinese dialectal terms
- Xiang Chinese
- Xiang terms with usage examples
- Japanese kanji
- Japanese hyōgai kanji
- Japanese kanji with goon reading し
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading し
- Japanese kanji with kun reading は
- Korean terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Middle Korean hanja
- Korean lemmas
- Korean hanja
- Korean hanja forms
- Vietnamese Chữ Hán
- Vietnamese lemmas
- Vietnamese Han characters
- Vietnamese Nom
- CJKV radicals

