止
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual[edit]
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
Alternative forms[edit]
Note that 龰 may also be a component of the radicals 疋 (𤴓/𤴔), 辵 (辶), 走, and 足 (𧾷).
Han character[edit]
止 (Kangxi radical 77, 止+0, 4 strokes, cangjie input 卜中一 (YLM), four-corner 21100, composition ⿱⿰丨⺊一 or ⿻上丨 or ⿻⺊丄)
- Kangxi radical #77, ⽌.
- Shuowen Jiezi radical №27
Derived characters[edit]
- Appendix:Chinese radical/止
- 𠇈, 𠯽, 址, 𪥧, 𭖇, 𢓊, 𪫣, 扯, 沚, 阯, 𨑭, 杫, 𣧐, 𪸔, 𭨪, 砋, 祉, 䄳, 𧘲, 䊼, 耻, 𧉀, 訨(𫟞), 𧺠, 趾, 𨊺, 䤠, 𩉮
- 𣢃, 𧠛, 頉, 𩾰, 𠂛, 企, 𭆨, 𧾷, 𫰏, 𫲺, 芷, 𭟰, 𪰊, 𦊆, 䇛, 𬯪, 𠹜, 𣥔, 𬈰, 𠣏, 𫧎, 𤵁, 凪, 𫭠, 𡵩, 𣏔, 肯, 𥎩, 𥘣, 𦙡, 𧉘, 𧖭, 𧣆, 𥎼, 𭪠, 𤉭, 齒(齿)
- 之, 足, 㢟, 延 (originally contain 止)
Descendants[edit]
- と (Hiragana character derived from Man'yōgana)
- ト (Katakana character derived from Man'yōgana)
References[edit]
- Kangxi Dictionary: page 573, character 24
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 16253
- Dae Jaweon: page 961, character 23
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 2, page 1435, character 3
- Unihan data for U+6B62
Chinese[edit]
| simp. and trad. |
止 | |
|---|---|---|
Glyph origin[edit]
| Historical forms of the character 止 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) | ||
| Bronze inscriptions | Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Chu slip and silk script | Qin slip script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |

|
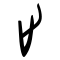
|

|

|

|

|

|
Pictogram (象形) – a footprint, originally meaning "foot". The derivative 趾 (OC *kjɯʔ) refers to the original meaning. Compare 手 (“hand”). Note that in oracle script, composed of 3 toes and a sole.
Compare to 夊, 夂, which have similar shape in oracle script, but pointing down (toe pointing right), and 𡕒 (as in right side of 舛, roughly ヰ, toe pointing left), hence different evolution.
Pronunciation[edit]
Definitions[edit]
止
- † foot
- to stop; to halt
- 休止 ― xiūzhǐ ― to stop
- to bring to an end; to stop; to relieve
- to end; to finish
- only (original form of 只 (zhǐ))
- 71st tetragram of the Taixuanjing (𝍌)
- (literary, archaic) Sentence-final particle indicating an emphasis.
Synonyms[edit]
- (to stop):
- 中斷/中断 (zhōngduàn)
- 中止 (zhōngzhǐ)
- 休止 (xiūzhǐ)
- 停 (tíng)
- 停歇 (tíngxiē)
- 停止 (tíngzhǐ)
- 夭閼/夭阏 (yǎo'è)
- 干休 (gānxiū) (literary)
- 放煞 (Min Nan)
- 斷站/断站 (Xiamen Hokkien)
- 斷節/断节 (Xiamen Hokkien)
- 暫停/暂停 (zàntíng) (temporarily)
- 歇 (xiē)
- 止息 (zhǐxī)
- 止煞 (Xiamen Hokkien, Zhangzhou Hokkien)
- 瀦/潴 (Quanzhou Hokkien)
- 煞 (Hokkien)
- 煞手 (Hokkien)
- 甘休 (gānxiū) (to be willing to give up)
- 終止/终止 (zhōngzhǐ)
- 絕/绝 (jué) (literary, or in compounds)
- 罷/罢
- 罷休/罢休 (bàxiū) (chiefly in the negative)
- 罷手/罢手 (bàshǒu)
- 間斷/间断
- 須/须 (xū) (literary)
- 頓/顿
Antonyms[edit]
- (antonym(s) of "stop"): 始 (shǐ)
Compounds[edit]
- 不止 (bùzhǐ)
- 中止 (zhōngzhǐ)
- 以戰止戰/以战止战
- 以殺止殺/以杀止杀
- 以湯止沸/以汤止沸
- 令行禁止 (lìngxíngjìnzhǐ)
- 休止 (xiūzhǐ)
- 仰止
- 休止符 (xiūzhǐfú)
- 何止 (hézhǐ)
- 停止 (tíngzhǐ)
- 制止 (zhìzhǐ)
- 動止/动止
- 勸止/劝止 (quànzhǐ)
- 古文觀止/古文观止 (Gǔwén Guānzhǐ)
- 吉祥止止
- 喝止 (hèzhǐ)
- 嘆為觀止/叹为观止 (tànwéiguānzhǐ)
- 大家舉止/大家举止
- 妨止
- 學無止境/学无止境 (xuéwúzhǐjìng)
- 官止神行
- 居止
- 底止
- 廢止/废止 (fèizhǐ)
- 心如止水 (xīnrúzhǐshuǐ)
- 戛然而止 (jiárán'érzhǐ)
- 戢止
- 截止 (jiézhǐ)
- 戾止
- 扇火止沸
- 投止
- 抑止 (yìzhǐ)
- 投膏止火
- 抽薪止沸
- 掛失止付/挂失止付
- 揚湯止沸/扬汤止沸 (yángtāngzhǐfèi)
- 摩訶止觀/摩诃止观
- 明德止善
- 暫止/暂止
- 望梅止渴 (wàngméizhǐkě)
- 望門投止/望门投止
- 棲止/栖止
- 欲言又止
- 歎為觀止/叹为观止 (tànwéiguānzhǐ)
- 止不住
- 止亂/止乱 (zhǐluàn)
- 止付
- 止住 (zhǐzhù)
- 止兌/止兑
- 止咳 (zhǐké)
- 止嘔/止呕
- 止境 (zhǐjìng)
- 止宿 (zhǐsù)
- 止息 (zhǐxī)
- 止惡揚善/止恶扬善 (zhǐ'èyángshàn)
- 止戈
- 止戈散馬/止戈散马
- 止戈為武/止戈为武 (zhǐgēwéiwǔ)
- 止戈興仁/止戈兴仁
- 止戰/止战
- 止持戒
- 止於至善/止于至善 (zhǐyúzhìshàn)
- 止暴禁非
- 止步 (zhǐbù)
- 止殺/止杀
- 止水 (zhǐshuǐ)
- 止泊
- 止渴 (zhǐkě)
- 止渴思梅
- 止渴飲鴆/止渴饮鸩
- 止痛 (zhǐtòng)
- 止痛藥/止痛药 (zhǐtòngyào)
- 止癢/止痒 (zhǐyǎng)
- 止血 (zhǐxuè)
- 止血劑/止血剂
- 止血帶/止血带 (zhǐxuèdài)
- 止血法
- 止血點/止血点
- 止觀/止观 (zhǐguān)
- 止詞/止词
- 止談風月/止谈风月
- 止謗/止谤
- 止足之分
- 止遏
- 止酒
- 止頓/止顿
- 歸止/归止
- 死而後止/死而后止
- 永無止境/永无止境 (yǒngwúzhǐjìng)
- 汐止 (xīzhǐ)
- 沒行止/没行止
- 流行坎止
- 淺嘗則止/浅尝则止
- 淺嘗輒止/浅尝辄止 (qiǎnchángzhézhǐ)
- 漫無止境/漫无止境
- 為止/为止 (wéizhǐ)
- 無止境/无止境 (wúzhǐjìng)
- 無行止/无行止
- 生津止渴
- 知止 (zhīzhǐ)
- 知足知止
- 禁止 (jìnzhǐ)
- 終止/终止 (zhōngzhǐ)
- 縱風止燎/纵风止燎
- 舉止/举止 (jǔzhǐ)
- 舉止不凡/举止不凡
- 舉止大方/举止大方
- 舉止失措/举止失措
- 舉止嫻雅/举止娴雅
- 舉止形容/举止形容
- 舉止言語/举止言语
- 舉止言談/举止言谈
- 舉止閑冶/举止闲冶
- 舉止風流/举止风流
- 舉止高雅/举止高雅
- 蒞止/莅止
- 蠅止/蝇止
- 行止 (xíngzhǐ)
- 補氣止血/补气止血
- 規行矩止/规行矩止
- 覯止/觏止
- 觀止/观止 (guānzhǐ)
- 言行舉止/言行举止
- 言談舉止/言谈举止 (yántánjǔzhǐ)
- 說梅止渴/说梅止渴
- 豈止/岂止 (qǐzhǐ)
- 進止/进止
- 遏止 (èzhǐ)
- 適可而止/适可而止 (shìkě'érzhǐ)
- 遮止
- 防止 (fángzhǐ)
- 阻止 (zǔzhǐ)
- 靜止/静止 (jìngzhǐ)
- 飲鴆止渴/饮鸩止渴 (yǐnzhènzhǐkě)
- 高山仰止 (gāoshānyǎngzhǐ)
- 高軒蒞止/高轩莅止
- 鳳止高梧/凤止高梧
- 點到為止/点到为止 (diǎndàowéizhǐ)
Japanese[edit]
Kanji[edit]
止
Readings[edit]
- Go-on: し (shi, Jōyō)
- Kan-on: し (shi, Jōyō)
- Kun: とまる (tomaru, 止まる, Jōyō); とめる (tomeru, 止める, Jōyō); とどまる (todomaru, 止まる); とどめる (todomeru, 止める); やむ (yamu, 止む); やめる (yameru, 止める); よす (yosu, 止す); さす (sasu, 止す)
Compounds[edit]
Compounds
- 止観 (shikan)
- 止汗剤 (shikanzai, “antiperspirant”)
- 止血 (shiketsu)
- 止止不須説 (shishifushusetsu)
- 止瀉剤 (shishazai, “antidiarrheal”)
- 止宿 (shishuku)
- 止住 (shijū)
- 止水 (shisui)
- 止痛 (shitsū)
- 止動方角 (shidōhōgaku)
- 止揚 (shiyō, “sublation”)
- 止痢剤 (shirizai)
- 止まり木 (tomarigi)
- 止句 (tomeku)
- 止相場 (tomesōba, “stop price”)
- 止め針, 止針 (tomebari, “pin”)
- 止偏 (tome-hen)
- 止め弁 (tomeben, “stop valve”)
- 遏止 (asshi)
- 駅止め (eki-dome, “delivery of freight by train”)
- 依止 (eji)
- 核抑止 (kakuyokushi, “nuclear deterrence”)
- 鎌止め (kama-dome, “prohibition on cutting grass”)
- 川止め (kawa-dome, “suspension of ferry service”)
- 諫止 (kanshi, “dissuasion”)
- 客止め (kyaku-dome, “full house”)
- 休止 (kyūshi)
- 競業避止 (kyōgyō hishi, “noncompete clause”)
- 挙止 (kyoshi, “bearing; deportment”)
- 拒止 (kyoshi, “refusal”)
- 禁止 (kinshi)
- 魚鳥止め (gyōchō-dome)
- 車止め (kuruma-dome, “buffer stop”)
- 車輪止め (sharin-dome, “chock”)
- 終止 (shūshi)
- 笑止 (shōshi)
- 進止 (shinshi)
- 制止 (seishi)
- 静止 (seishi)
- 咳止め (seki-dome, “cough medicine”)
- 阻止, 沮止 (soshi)
- 体言止め (taigen-dome)
- 血止め (chi-dome, “styptic”)
- 中止 (chūshi)
- 丁々発止 (chōchōhasshi)
- 停止 (teishi)
- 底止 (teishi)
- 動止 (dōshi)
- 廃止 (haishi)
- 波止場 (hatoba)
- 閉止 (heishi, “stoppage”)
- 防止 (bōshi)
- 明鏡止水 (meikyōshisui)
- 黙止 (mokushi, “keeping quiet”)
- 山止め (yama-dome, “landslide prevention wall”)
- 雪止め (yuki-dome, “snow guard, snow stopper”)
- 容止 (yōshi)
- 抑止 (yokushi)
- 乎古止点 (okototen)
Korean[edit]
Hanja[edit]
Vietnamese[edit]
Han character[edit]
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.
Categories:
- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Kangxi Radicals block
- Han character radicals
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- Shuowen radicals
- Han pictograms
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Gan lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Jin lemmas
- Northern Min lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Xiang lemmas
- Chinese nouns
- Mandarin nouns
- Cantonese nouns
- Gan nouns
- Hakka nouns
- Jin nouns
- Northern Min nouns
- Eastern Min nouns
- Hokkien nouns
- Teochew nouns
- Wu nouns
- Xiang nouns
- Chinese verbs
- Mandarin verbs
- Cantonese verbs
- Gan verbs
- Hakka verbs
- Jin verbs
- Northern Min verbs
- Eastern Min verbs
- Hokkien verbs
- Teochew verbs
- Wu verbs
- Xiang verbs
- Chinese adverbs
- Mandarin adverbs
- Cantonese adverbs
- Gan adverbs
- Hakka adverbs
- Jin adverbs
- Northern Min adverbs
- Eastern Min adverbs
- Hokkien adverbs
- Teochew adverbs
- Wu adverbs
- Xiang adverbs
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese Han characters
- Chinese terms with obsolete senses
- Mandarin terms with usage examples
- Chinese literary terms
- Chinese terms with archaic senses
- Elementary Mandarin
- Japanese Han characters
- Grade 2 kanji
- Japanese kanji with goon reading し
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading し
- Japanese kanji with kun reading と-まる
- Japanese kanji with kun reading と-める
- Japanese kanji with kun reading とど-まる
- Japanese kanji with kun reading とど-める
- Japanese kanji with kun reading や-む
- Japanese kanji with kun reading や-める
- Japanese kanji with kun reading よ-す
- Japanese kanji with kun reading さ-す
- Korean lemmas
- Korean Han characters
- Vietnamese lemmas
- Vietnamese Han characters
- CJKV radicals
