向
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| ||||||||
Translingual[edit]
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Han character[edit]
向 (Kangxi radical 30, 口+3, 6 strokes, cangjie input 竹月口 (HBR), four-corner 27220, composition ⿱丿冋 or ⿵𰃦口)
Derived characters[edit]
References[edit]
- Kangxi Dictionary: page 176, character 4
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 3301
- Dae Jaweon: page 393, character 4
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 1, page 579, character 8
- Unihan data for U+5411
Chinese[edit]
Glyph origin[edit]
| Historical forms of the character 向 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Chu slip and silk script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |

|

|

|
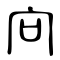
|

|
Ideogrammic compound (會意/会意) : 宀 (“house”) + 口 (“mouth”), echos in a place. The original form of 響. It was borrowed to represent 𠨍 (嚮) later.
Etymology 1[edit]
| simp. and trad. |
向 | |
|---|---|---|
- “ACG: for (directed at, intended to belong to)”
- Orthographic borrowing from Japanese 向け (muke).
Pronunciation 1[edit]
Definitions[edit]
向
- to face
- to side with; to favour; to discriminate in favour of
- (literary) to admire; to revere
- (literary) to approach; to advance towards
- 向晚 ― xiàngwǎn ― evening
- direction
- towards; to
- (literary) the old days; the past
- always; throughout
- (Taivoan religious concept) sorcery, taboo, and magic
- (chiefly ACG, suffix forming attributive adjectives) for (directed at, intended to belong to)
- 子供向 ― zǐgōngxiàng ― family-friendly (literally, “for children”)
- 催淚向/催泪向 ― cuīlèixiàng ― tearjerker
Compounds[edit]
- 一向 (yīxiàng)
- 不可向邇/不可向迩 (bùkěxiàng'ěr)
- 不知去向 (bùzhīqùxiàng)
- 人心向背 (rénxīnxiàngbèi)
- 人心所向 (rénxīnsuǒxiàng)
- 偏向 (piānxiàng)
- 傾向/倾向
- 內向/内向 (nèixiàng)
- 共同趨向/共同趋向
- 出口導向/出口导向
- 分向島/分向岛
- 劉向/刘向
- 動向/动向 (dòngxiàng)
- 去向 (qùxiàng)
- 反向 (fǎnxiàng)
- 反方向 (fǎnfāngxiàng)
- 取向 (qǔxiàng)
- 向上 (xiàngshàng)
- 向下 (xiàngxià)
- 向使 (xiàngshǐ)
- 向例
- 向來/向来 (xiànglái)
- 向光 (xiàngguāng)
- 向光性
- 向前 (xiàngqián)
- 向化
- 向北 (xiàngběi)
- 向午
- 向善 (xiàngshàn)
- 向地性
- 向壁虛構/向壁虚构 (xiàngbìxūgòu)
- 向壁虛造/向壁虚造 (xiàngbìxūzào)
- 向外 (xiàngwài)
- 向學/向学 (xiàngxué)
- 向寵/向宠
- 向導/向导 (xiàngdǎo)
- 向平之願/向平之愿
- 向年
- 向往 (xiàngwǎng)
- 向後/向后 (xiànghòu)
- 向心力 (xiàngxīnlì)
- 向心花序
- 向斜層/向斜层
- 向日 (xiàngrì)
- 向日性
- 向日葵 (xiàngrìkuí)
- 向時/向时 (xiàngshí)
- 向晚 (xiàngwǎn)
- 向暮 (xiàngmù)
- 向曉/向晓
- 向望 (ǹg-bāng) (Min Nan)
- 向東/向东 (xiàngdōng)
- 向格 (xiànggé)
- 向榮/向荣
- 向溼性/向湿性
- 向火
- 向火乞兒/向火乞儿
- 向當/向当
- 向盤/向盘 (xiàngpán)
- 向秀
- 向聲背實/向声背实
- 向背 (xiàngbèi)
- 向著/向着 (xiàngzhe)
- 向西 (xiàngxī)
- 向量 (xiàngliàng)
- 向錢看/向钱看
- 向隅 (xiàngyú)
- 向陽/向阳 (xiàngyáng)
- 向隅獨泣/向隅独泣 (xiàngyúdúqì)
- 向隅而泣 (xiàngyú'érqì)
- 向電性/向电性
- 向非
- 向順/向顺
- 向風/向风
- 單向/单向 (dānxiàng)
- 單向天線/单向天线
- 單向道/单向道 (dānxiàngdào)
- 外向 (wàixiàng)
- 大方向 (dàfāngxiàng)
- 奈向
- 奮發向上/奋发向上
- 定向 (dìngxiàng)
- 定向天線/定向天线
- 導向/导向 (dǎoxiàng)
- 導向思考/导向思考
- 導向飛彈/导向飞弹 (dǎoxiàng fēidàn)
- 導向魚雷/导向鱼雷
- 山向
- 志向 (zhìxiàng)
- 性向 (xìngxiàng)
- 性向測驗/性向测验
- 怒目相向
- 意向 (yìxiàng)
- 所向披靡
- 所向無前/所向无前
- 所向無敵/所向无敌 (suǒxiàngwúdí)
- 投向 (tóuxiàng)
- 折節向學/折节向学
- 指向 (zhǐxiàng)
- 改惡向善/改恶向善
- 改過向善/改过向善
- 斐然向風/斐然向风
- 方向 (fāngxiàng)
- 方向燈/方向灯
- 方向盤/方向盘 (fāngxiàngpán)
- 方向舵 (fāngxiàngduò)
- 昏頭轉向/昏头转向
- 暈頭轉向/晕头转向
- 朝向 (cháoxiàng)
- 東向/东向
- 東奔西向/东奔西向
- 橫向/横向 (héngxiàng)
- 欣欣向榮/欣欣向荣 (xīnxīnxiàngróng)
- 歸向/归向 (guīxiàng)
- 歸向導引/归向导引
- 民心趨向/民心趋向
- 民意向背
- 無計向/无计向
- 物件導向/物件导向
- 特殊性向
- 發憤向上/发愤向上
- 相向 (xiāngxiàng)
- 看風向/看风向
- 矇頭轉向/蒙头转向
- 矛盾相向
- 航向
- 蘄向/蕲向
- 護向/护向
- 走向 (zǒuxiàng)
- 趨向/趋向 (qūxiàng)
- 轉向/转向
- 迎向
- 逆向 (nìxiàng)
- 迴向/回向
- 逆向公車/逆向公车
- 逆向思考
- 逆向整合
- 邁向/迈向 (màixiàng)
- 鋒芒所向/锋芒所向
- 雙向/双向 (shuāngxiàng)
- 雙向溝通/双向沟通
- 震旦方向
- 靡然向風/靡然向风
- 風向/风向 (fēngxiàng)
- 風向標/风向标 (fēngxiàngbiāo)
- 風向球/风向球
- 風向袋/风向袋
Descendants[edit]
Pronunciation 2[edit]
Definitions[edit]
向
Etymology 2[edit]
| For pronunciation and definitions of 向 – see 嚮 (“to turn toward; to approach; toward; facing; against; etc.”). (This character is the simplified and ancient form of 嚮). |
Notes:
|
Etymology 3[edit]
| For pronunciation and definitions of 向 – see 曏 (“in the near past; in the past; formerly; facing; against; etc.”). (This character is the simplified form of 曏). |
Notes:
|
Japanese[edit]
Kanji[edit]
向
Readings[edit]
- Go-on: こう (kō, Jōyō)←かう (kau, historical)
- Kan-on: きょう (kyō)←きやう (kyau, historical)
- Kun: むかう (mukau, 向かう, Jōyō)←むかふ (mukafu, 向かふ, historical); むく (muku, 向く, Jōyō); むける (mukeru, 向ける, Jōyō); むこう (mukō, 向こう, Jōyō); さきに (sakini, 向に); むかい (mukai, 向かい)←むかひ (mukafi, 向かひ, historical); むき (muki, 向き)
- Nanori: ひさ (hisa); むか (muka); むかう (mukau); むき (muki); むけ (muke); むこう (mukō); しょう (shō)←しやう (syau, historical)
Compounds[edit]
- 向後 (kyōgo)
- 向後 (kyōkō)
- 向日 (kyōjitsu) (嚮日)
- 向日葵 (kyōjikki)
- 向者 (kyōsha) (嚮者)
- 向前 (kyōzen) (嚮前)
- 向明 (kyōmei) (嚮明)
- 向来 (kyōrai) (嚮来)
- 向学 (kōgaku)
- 向寒 (kōkan)
- 向後 (kōgo)
- 向日 (kōjitsu) (嚮日)
- 向日葵 (kōjikki)
- 向暑 (kōsho)
- 向上 (kōjō)
- 向性 (kōsei)
- 向背 (kōhai) (嚮背)
- 向拝 (gohai)
- 向日葵 (himawari)
- 向三軒両隣 (mukōsangen ryōdonari)
- 意向 (ikō) (意嚮)
- 一向 (ikkō)
- 回向, 廻向 (ekō)
- 外向 (gaikō)
- 葵向 (kikō)
- 傾向 (keikō)
- 下向 (gekō)
- 参向 (sankō)
- 志向 (shikō)
- 指向 (shikō)
- 趣向 (shukō)
- 出向 (shukkō)
- 趨向 (sūkō)
- 性向 (seikō)
- 対向 (taikō)
- 手向 (tamuke)
- 転向 (tenkō)
- 動向 (dōkō)
- 内向 (naikō)
- 発向 (hakkō)
- 日向 (hinata)
- 風向 (fūkō)
- 偏向 (henkō)
- 方向 (hōkō)
- 真っ向 (makkō)
- 影向 (yōgō)
Proper noun[edit]
- a surname
Korean[edit]
Etymology 1[edit]
Hanja[edit]
向 (eumhun 향할 향 (hyanghal hyang))
Etymology 2[edit]
Hanja[edit]
Vietnamese[edit]
Han character[edit]
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}.
Categories:
- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- Han ideogrammic compounds
- Chinese terms borrowed from Japanese
- Chinese orthographic borrowings from Japanese
- Chinese terms derived from Japanese
- Mandarin terms with audio links
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Sichuanese lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Chinese verbs
- Mandarin verbs
- Sichuanese verbs
- Cantonese verbs
- Hakka verbs
- Eastern Min verbs
- Hokkien verbs
- Teochew verbs
- Wu verbs
- Chinese nouns
- Mandarin nouns
- Sichuanese nouns
- Cantonese nouns
- Hakka nouns
- Eastern Min nouns
- Hokkien nouns
- Teochew nouns
- Wu nouns
- Chinese prepositions
- Mandarin prepositions
- Sichuanese prepositions
- Cantonese prepositions
- Hakka prepositions
- Eastern Min prepositions
- Hokkien prepositions
- Teochew prepositions
- Wu prepositions
- Chinese adverbs
- Mandarin adverbs
- Sichuanese adverbs
- Cantonese adverbs
- Hakka adverbs
- Eastern Min adverbs
- Hokkien adverbs
- Teochew adverbs
- Wu adverbs
- Chinese suffixes
- Mandarin suffixes
- Sichuanese suffixes
- Cantonese suffixes
- Hakka suffixes
- Eastern Min suffixes
- Hokkien suffixes
- Teochew suffixes
- Wu suffixes
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese Han characters
- Mandarin terms with usage examples
- Chinese literary terms
- Chinese fandom slang
- Mandarin terms with collocations
- Chinese proper nouns
- Mandarin proper nouns
- Cantonese proper nouns
- Hokkien proper nouns
- zh:Historical polities
- zh:Places in Shandong
- zh:Places in China
- Chinese surnames
- Literary Chinese terms with quotations
- Chinese simplified forms
- Beginning Mandarin
- Japanese Han characters
- Grade 3 kanji
- Japanese kanji with goon reading こう
- Japanese kanji with historical goon reading かう
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading きょう
- Japanese kanji with historical kan'on reading きやう
- Japanese kanji with kun reading む-かう
- Japanese kanji with historical kun reading む-かふ
- Japanese kanji with kun reading む-く
- Japanese kanji with kun reading む-ける
- Japanese kanji with kun reading む-こう
- Japanese kanji with kun reading さき-に
- Japanese kanji with kun reading む-かい
- Japanese kanji with historical kun reading む-かひ
- Japanese kanji with kun reading む-き
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ひさ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading むか
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading むかう
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading むき
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading むけ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading むこう
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading しょう
- Japanese kanji with historical nanori reading しやう
- Japanese lemmas
- Japanese proper nouns
- Japanese terms spelled with third grade kanji
- Japanese terms written with one Han script character
- Japanese terms spelled with 向
- Japanese single-kanji terms
- Japanese surnames
- Korean lemmas
- Korean Han characters
- Korean surnames
- Vietnamese lemmas
- Vietnamese Han characters