音
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual
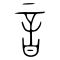
[edit]| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
Han character
[edit]音 (Kangxi radical 180, 音+0, 9 strokes, cangjie input 卜廿日 (YTA), four-corner 00601, composition ⿱立日 or ⿱亠𣅑)
- Kangxi radical #180, ⾳.
- Shuowen Jiezi radical №58
Derived characters
[edit]- Appendix:Chinese radical/音
- 偣, 𠗥, 喑, 堷, 㛺, 𡺈, 𢄈, 愔, 揞, 摿, 湆, 𤟟, 隌, 暗, 𪳀, 𬇂, 𤋾, 腤, 𥚱, 𤭵, 𪾲, 𥏮, 䅧, 𥻚, 𦂺, 𦖢, 諳(谙), 䜾, 𮛾, 𨍑, 䤃, 𮢣, 𩈴, 𮧡, 䬓(𫗊), 𩩿, 𬛯, 𩹎, 黯, 𩆢, 𥃛, 𪛏
- 𪟠, 𫦊, 戠, 𢻕, 𢾑, 𢾚, 歆, 𪵦, 𫅬, 𧡱, 𧯹, 𪱐, 鶕(𬸝), 𥃚, 意, 𡩘, 𡺞, 萻, 窨, 罯, 𦋫, 𩄒, 𩮋, 𪔧, 𩇄, 𫨏, 𢉩, 瘖, 闇(𬮴), 𧗹, 𫭏
References
[edit]- Kangxi Dictionary: page 1396, character 25
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 43265
- Dae Jaweon: page 1912, character 16
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 7, page 4495, character 1
- Unihan data for U+97F3
Chinese
[edit]| simp. and trad. |
音 | |
|---|---|---|
Glyph origin
[edit]| Historical forms of the character 音 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western Zhou | Spring and Autumn | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) | |
| Bronze inscriptions | Bronze inscriptions | Chu slip and silk script | Qin slip script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |

|
|

|

|

|

|
Ideogram (指事) : 言 (“word”) with something in 口 (“mouth”) – sound comes from the mouth.
Pronunciation
[edit]- Mandarin
- (Standard)
- (Chengdu, Sichuanese Pinyin): yin1
- (Dungan, Cyrillic and Wiktionary): йин (yin, I)
- Cantonese
- Gan (Wiktionary): in1
- Hakka
- Jin (Wiktionary): ing2 / ing1
- Northern Min (KCR): éng
- Eastern Min (BUC): ĭng
- Southern Min
- Wu (Shanghai, Wugniu): 1in
- Xiang (Changsha, Wiktionary): in1
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Hanyu Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄧㄣ
- Tongyong Pinyin: yin
- Wade–Giles: yin1
- Yale: yīn
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: in
- Palladius: инь (inʹ)
- Sinological IPA (key): /in⁵⁵/
- (Chengdu)
- Sichuanese Pinyin: yin1
- Scuanxua Ladinxua Xin Wenz: in
- Sinological IPA (key): /in⁵⁵/
- (Dungan)
- Cyrillic and Wiktionary: йин (yin, I)
- Sinological IPA (key): /iŋ²⁴/
- (Note: Dungan pronunciation is currently experimental and may be inaccurate.)
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Jyutping: jam1
- Yale: yām
- Cantonese Pinyin: jam1
- Guangdong Romanization: yem1
- Sinological IPA (key): /jɐm⁵⁵/
- (Taishanese, Taicheng)
- Wiktionary: yim1
- Sinological IPA (key): /jim³³/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Gan
- (Nanchang)
- Wiktionary: in1
- Sinological IPA (key): /in⁴²/
- (Nanchang)
- Hakka
- (Northern Sixian, incl. Miaoli)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: yîm
- Hakka Romanization System: im´
- Hagfa Pinyim: yim1
- Sinological IPA: /im²⁴/
- (Southern Sixian, incl. Meinong)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: yîm
- Hakka Romanization System: (r)im´
- Hagfa Pinyim: yim1
- Sinological IPA: /(j)im²⁴/
- (Meixian)
- (Northern Sixian, incl. Miaoli)
- Jin
- (Taiyuan)+
- Wiktionary: ing2 / ing1
- Sinological IPA (old-style): /ĩŋ⁵³/, /ĩŋ¹¹/
- (Taiyuan)+
- ing2 in 音訊;
- ing1 in 聲音.
- Northern Min
- (Jian'ou)
- Kienning Colloquial Romanized: éng
- Sinological IPA (key): /eiŋ⁵⁴/
- (Jian'ou)
- Eastern Min
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: ĭng
- Sinological IPA (key): /iŋ⁵⁵/
- (Fuzhou)
- Southern Min
- Dialectal data
| Variety | Location | 音 |
|---|---|---|
| Mandarin | Beijing | /in⁵⁵/ |
| Harbin | /in⁴⁴/ | |
| Tianjin | /in²¹/ | |
| Jinan | /iẽ²¹³/ | |
| Qingdao | /iə̃²¹³/ | |
| Zhengzhou | /in²⁴/ | |
| Xi'an | /iẽ²¹/ | |
| Xining | /iə̃⁴⁴/ | |
| Yinchuan | /iŋ⁴⁴/ | |
| Lanzhou | /ĩn³¹/ | |
| Ürümqi | /iŋ⁴⁴/ | |
| Wuhan | /in⁵⁵/ | |
| Chengdu | /in⁵⁵/ | |
| Guiyang | /in⁵⁵/ | |
| Kunming | /ĩ⁴⁴/ | |
| Nanjing | /in³¹/ | |
| Hefei | /in²¹/ | |
| Jin | Taiyuan | /iəŋ¹¹/ |
| Pingyao | /iŋ¹³/ | |
| Hohhot | /ĩŋ³¹/ | |
| Wu | Shanghai | /iŋ⁵³/ |
| Suzhou | /in⁵⁵/ | |
| Hangzhou | /ʔin³³/ | |
| Wenzhou | /j̠aŋ³³/ | |
| Hui | Shexian | /iʌ̃³¹/ |
| Tunxi | /in¹¹/ | |
| Xiang | Changsha | /in³³/ |
| Xiangtan | /in³³/ | |
| Gan | Nanchang | /in⁴²/ |
| Hakka | Meixian | /im⁴⁴/ |
| Taoyuan | /im²⁴/ | |
| Cantonese | Guangzhou | /jɐm⁵³/ |
| Nanning | /jɐm⁵⁵/ | |
| Hong Kong | /jɐm⁵⁵/ | |
| Min | Xiamen (Hokkien) | /im⁵⁵/ |
| Fuzhou (Eastern Min) | /iŋ⁴⁴/ | |
| Jian'ou (Northern Min) | /eiŋ⁵⁴/ | |
| Shantou (Teochew) | /im³³/ | |
| Haikou (Hainanese) | /im²³/ |
- Middle Chinese: 'im
- Old Chinese
- (Baxter–Sagart): /*[q](r)əm/
- (Zhengzhang): /*qrɯm/
Definitions
[edit]音
- sound; voice; tone
- 音障 ― yīnzhàng ― sound barrier
- news; tidings
- (music) pitch; note (Classifier: 粒 c)
- (phonetics) pronunciation; syllable
Synonyms
[edit]- (sound):
Compounds
[edit]- 一口同音
- 一槌定音 (yīchuídìngyīn)
- 一錘定音/一锤定音 (yīchuídìngyīn)
- 一音
- 一音教
- 七音 (qīyīn)
- 三妙音
- 三拼音
- 不帶音/不带音
- 不送氣音/不送气音 (bùsòngqìyīn)
- 中原音韻/中原音韵 (Zhōngyuán Yīnyùn)
- 中州音韻/中州音韵
- 中音 (zhōngyīn)
- 中音提琴
- 主元音
- 主調音/主调音
- 主音 (zhǔyīn)
- 久音
- 九音鑼/九音锣
- 乾音/干音
- 五音 (wǔyīn)
- 五音不全 (wǔyīnbùquán)
- 五音兒/五音儿
- 五音士
- 五音戲/五音戏
- 亡國之音/亡国之音 (wángguó zhī yīn)
- 京音大鼓
- 今音 (jīnyīn)
- 介音 (jièyīn)
- 令音
- 仙音
- 仙音燭/仙音烛
- 仙音院
- 伉音
- 低元音
- 佛教音樂/佛教音乐
- 低音 (dīyīn)
- 低音提琴 (dīyīn tíqín)
- 佳音 (jiāyīn)
- 便音
- 促音 (cùyīn)
- 信音
- 俞音
- 俊音
- 借音
- 傒音
- 傳音快字/传音快字
- 儂音/侬音
- 元音 (yuányīn)
- 光學錄音/光学录音
- 光音
- 光音天
- 光音王
- 兌音/兑音
- 兒化音/儿化音 (érhuàyīn)
- 全閉音/全闭音
- 全音 (quányīn)
- 八分音符 (bāfēn yīnfú)
- 八度音程
- 八音 (bāyīn)
- 八音匣
- 八音子
- 八音手槍/八音手枪
- 八音會/八音会
- 八音琴
- 八音盒 (bāyīnhé)
- 八音盒子
- 八音聯歡/八音联欢
- 八音遏密
- 八音響/八音响
- 八音領袖/八音领袖
- 六犯清音
- 凡音
- 凶音
- 切分音
- 分音
- 切音
- 前元音
- 北鄙之音
- 北音
- 千手觀音/千手观音
- 半低元音
- 半元音 (bànyuányīn)
- 半合元音
- 半抖音
- 半母音 (bànmǔyīn)
- 半舌音
- 半閉元音/半闭元音
- 半開元音/半开元音
- 半音 (bànyīn)
- 半音階/半音阶 (bànyīnjiē)
- 半高元音
- 半齒音/半齿音
- 協音/协音
- 南音 (nányīn)
- 卷舌元音
- 卷舌音 (juǎnshéyīn)
- 原音帶/原音带
- 厲音/厉音
- 反音
- 口音 (kǒuyīn)
- 古典音樂/古典音乐 (gǔdiǎn yīnyuè)
- 句重音
- 古音 (gǔyīn)
- 合元音
- 合口元音
- 同期錄音/同期录音
- 同步錄音/同步录音
- 吐氣音/吐气音
- 合音 (héyīn)
- 吐音
- 同音 (tóngyīn)
- 同音共律
- 合音字
- 同音詞/同音词 (tóngyīncí)
- 吳音/吴音 (wúyīn)
- 呼吸音 (hūxīyīn)
- 和音 (héyīn)
- 呼音
- 哀音
- 咬音咂字
- 唇音 (chúnyīn)
- 哨音
- 唄音/呗音
- 唐音 (tángyīn)
- 唇齒音/唇齿音 (chúnchǐyīn)
- 商音
- 單元音/单元音 (dānyuányīn)
- 喉塞音
- 喉擦音
- 喉音 (hóuyīn)
- 喪音/丧音
- 單音奏法/单音奏法
- 單音程/单音程
- 單音詞/单音词
- 單音語/单音语
- 嗣音
- 嗓音 (sǎngyīn)
- 嗡鼻音
- 嘉音
- 嘈音
- 嘵音瘏口/哓音瘏口
- 噪音 (zàoyīn)
- 噭音
- 噪音汙染/噪音污染 (zàoyīn wūrǎn)
- 噪音音樂/噪音音乐
- 囂音/嚣音
- 四分音符 (sìfēn yīnfú)
- 回音 (huíyīn)
- 固定重音
- 國語配音/国语配音
- 國際音標/国际音标 (guójì yīnbiāo)
- 國音/国音 (guóyīn)
- 國音字母/国音字母
- 圓脣元音/圆唇元音
- 圓音/圆音
- 團音/团音
- 土音 (tǔyīn)
- 坎音
- 垂音
- 基礎音/基础音
- 堂音
- 基音 (jīyīn)
- 塞擦音 (sècāyīn)
- 塞爆音
- 塞音
- 塵音/尘音
- 多軌錄音/多轨录音 (duōguǐ lùyīn)
- 多音字 (duōyīnzì)
- 大音
- 大音希聲/大音希声 (dàyīnxīshēng)
- 大音階/大音阶 (dàyīnjiē)
- 太音
- 央元音 (yāngyuányīn)
- 失音 (shīyīn)
- 夷音
- 女高音 (nǚgāoyīn)
- 如奉綸音/如奉纶音
- 好音
- 妙音 (miàoyīn)
- 妍音
- 威音
- 威音王佛
- 子音 (zǐyīn)
- 字音 (zìyīn)
- 孤音
- 宗教音樂/宗教音乐
- 官音
- 定音鼓 (dìngyīngǔ)
- 客家八音
- 宮庭音樂/宫庭音乐
- 宸音
- 宮音/宫音
- 寄音
- 寒音
- 實音/实音
- 審音/审音
- 小音階/小音阶 (xiǎoyīnjiē)
- 尖元音
- 尖團音/尖团音 (jiāntuányīn)
- 尖音
- 尾音 (wěiyīn)
- 展脣元音/展唇元音
- 屬音/属音 (shǔyīn)
- 巫音
- 巴音郭楞 (Bāyīnguōléng)
- 希音
- 常音
- 帶音/带音 (dàiyīn)
- 幾音/几音
- 庸音
- 廟瑟音/庙瑟音
- 弄音
- 弦外之音 (xiánwàizhīyīn)
- 弦外有音
- 弦音
- 強音/强音
- 彈音/弹音 (tányīn)
- 影音光碟 (yǐngyīn guāngdié)
- 影音統碟/影音统碟
- 徂音
- 後元音/后元音 (hòuyuányīn)
- 復音/复音
- 微音
- 微音器 (wēiyīnqì)
- 徵音/征音
- 德音
- 德音莫違/德音莫违
- 徽音
- 心雜音/心杂音 (xīnzáyīn)
- 心靈音樂/心灵音乐
- 心音 (xīnyīn)
- 心音圖/心音图
- 悲音
- 惠音
- 感音
- 成音
- 托音
- 抗音
- 抖音 (dǒuyīn)
- 拏音/拿音
- 拍音
- 按音 (ànyīn)
- 挐音
- 拼音 (pīnyīn)
- 拼音字母 (pīnyīn zìmǔ)
- 拼音文字 (pīnyīn wénzì)
- 捲舌元音/卷舌元音
- 捲舌音/卷舌音 (juǎnshéyīn)
- 捷音
- 揚音/扬音
- 摩擦音 (mócāyīn)
- 播音 (bōyīn)
- 播音員/播音员 (bōyīnyuán)
- 擇音/择音
- 擦音 (cāyīn)
- 擬音/拟音 (nǐyīn)
- 擴音/扩音 (kuòyīn)
- 擴音器/扩音器 (kuòyīnqì)
- 攝音/摄音
- 收錄音機/收录音机
- 收音 (shōuyīn)
- 收音機/收音机 (shōuyīnjī)
- 放音機/放音机
- 散音 (sànyīn)
- 敲擊音樂/敲击音乐
- 新音
- 方音 (fāngyīn)
- 早賜玉音/早赐玉音
- 暫音/暂音
- 曼音
- 有音無字/有音无字 (yǒuyīnwúzì)
- 朝音
- 杳無音信/杳无音信 (yǎowúyīnxìn)
- 杳無音耗/杳无音耗
- 杳無音訊/杳无音讯 (yǎowúyīnxùn)
- 松音
- 東音/东音
- 桑間之音/桑间之音 (sāngjiānzhīyīn)
- 桐音
- 梵音 (fànyīn)
- 梟音/枭音
- 棲音/栖音
- 極音/极音
- 楚音
- 標準元音/标准元音
- 標準音/标准音 (biāozhǔnyīn)
- 樂音/乐音 (yuèyīn)
- 標音法/标音法
- 標題音樂/标题音乐 (biāotí yīnyuè)
- 次重音
- 歌音
- 正始之音
- 正始音
- 正聲雅音/正声雅音
- 正音 (zhèngyīn)
- 正音法
- 殊音
- 母音 (mǔyīn)
- 比音
- 民俗音樂/民俗音乐
- 民族音樂/民族音乐
- 水月觀音/水月观音
- 水音兒/水音儿
- 沖音/冲音
- 沈音
- 泮林革音
- 注音 (zhùyīn)
- 法音
- 波音 (Bōyīn)
- 泉音
- 泛音 (fànyīn)
- 注音符號 (zhùyīn fúhào)
- 活觀音/活观音
- 洪音
- 流音 (liúyīn)
- 海潮音
- 消音 (xiāoyīn)
- 浮音
- 消音器 (xiāoyīnqì)
- 淫音
- 混音 (hùnyīn)
- 清音 (qīngyīn)
- 清音居士
- 渺無音信/渺无音信
- 渺無音訊/渺无音讯
- 滑音 (huáyīn)
- 溺音
- 滅音器/灭音器
- 漢音/汉音 (hànyīn)
- 潮音 (cháoyīn)
- 潮音洞
- 濁音/浊音 (zhuóyīn)
- 濮上之音 (púshàngzhīyīn)
- 灌音
- 無音/无音 (wúyīn)
- 熱門音樂/热门音乐
- 爆發音/爆发音 (bàofāyīn)
- 爨下音
- 爵士音樂/爵士音乐 (juéshì yīnyuè)
- 牙音 (yáyīn)
- 物音
- 狼音 (lángyīn)
- 獻仙音/献仙音
- 玄音
- 王音
- 玉音 (yùyīn)
- 理音
- 球音
- 琶音 (páyīn)
- 琴音
- 瑤華音/瑶华音
- 瑤音/瑶音
- 瓊音/琼音
- 男中音 (nánzhōngyīn)
- 男低音
- 男高音 (nángāoyīn)
- 留音機/留音机
- 異口同音/异口同音
- 異音/异音
- 畫外音/画外音 (huàwàiyīn)
- 疏音
- 痛失知音
- 瘁音
- 瘏口嘵音/瘏口哓音
- 發音/发音 (fāyīn)
- 發音器官/发音器官
- 發音學/发音学
- 發音方法/发音方法
- 發音部位/发音部位
- 發音障礙/发音障碍 (fāyīn zhàng'ài)
- 白衣觀音/白衣观音
- 白雪遺音/白雪遗音
- 的音
- 直音 (zhíyīn)
- 眠音
- 眾啄同音/众啄同音
- 知音 (zhīyīn)
- 知音諳呂/知音谙吕
- 知音識趣/知音识趣
- 短音 (duǎnyīn)
- 石音
- 破裂音 (pòlièyīn)
- 破音字
- 確音/确音
- 福音 (fúyīn)
- 福音堂
- 福音書/福音书 (fúyīnshū)
- 秋音
- 空谷足音
- 空谷跫音
- 空音
- 立體音響/立体音响
- 笑音
- 笙磬同音
- 笳音
- 筆音/笔音
- 管音
- 糜糜之音 (mímízhīyīn)
- 約翰福音/约翰福音 (Yuēhàn Fúyīn)
- 素音
- 納音/纳音
- 純音/纯音
- 絃外之音/弦外之音 (xiánwàizhīyīn)
- 絃外遺音/弦外遗音
- 絃外音/弦外音
- 細音/细音
- 絕對音感/绝对音感 (juéduìyīngǎn)
- 絕對音樂/绝对音乐 (juéduì yīnyuè)
- 緒音/绪音
- 綸音/纶音
- 綸音佛語/纶音佛语
- 緘音/缄音
- 緩音/缓音
- 繁音
- 繁音促節/繁音促节
- 繞梁之音
- 翰音
- 翹舌音/翘舌音
- 耗音
- 耶魯拼音/耶鲁拼音 (Yēlǔ pīnyīn)
- 聆音
- 聆音察理
- 聲音/声音 (shēngyīn)
- 聲音笑貌/声音笑貌
- 聽音哨/听音哨
- 背景音樂/背景音乐 (bèijǐng yīnyuè)
- 脣音/唇音 (chúnyīn)
- 脣齒音/唇齿音 (chúnchǐyīn)
- 腔音
- 腐音
- 膛音
- 自然音程
- 至音
- 舉音/举音
- 舌尖元音
- 舌尖前音 (shéjiānqiányīn)
- 舌尖後音/舌尖后音
- 舌尖邊音/舌尖边音
- 舌尖音 (shéjiānyīn)
- 舌尖鼻音
- 舌根音
- 舌根鼻音
- 舌葉音/舌叶音 (shéyèyīn)
- 舌面元音
- 舌面前音
- 舌面後音/舌面后音
- 舌面音
- 舌音 (shéyīn)
- 舌齒音/舌齿音
- 艮音
- 芳音
- 英音
- 落音
- 蕪音/芜音
- 號音/号音
- 蠻音/蛮音
- 表音 (biǎoyīn)
- 表音文字 (biǎoyīn wénzì)
- 衷音
- 裁音
- 裝飾音/装饰音 (zhuāngshìyīn)
- 複元音/复元音 (fùyuányīn)
- 複合元音/复合元音
- 複輔音/复辅音 (fùfǔyīn)
- 複音/复音 (fùyīn)
- 複音詞/复音词
- 西音
- 覆音
- 覺音/觉音
- 觀世音/观世音 (Guānshìyīn)
- 觀音/观音 (Guānyīn)
- 觀音佛祖/观音佛祖
- 觀音兜/观音兜
- 觀音土/观音土 (Guānyīntǔ)
- 觀音壋/观音垱 (Guānyīndàng)
- 觀音大士/观音大士 (Guānyīn Dàshì)
- 觀音媽/观音妈
- 觀音山/观音山
- 觀音座蓮/观音座莲
- 觀音庵/观音庵
- 觀音手/观音手
- 觀音柳/观音柳
- 觀音棕竹/观音棕竹
- 觀音法會/观音法会
- 觀音竹/观音竹 (guānyīnzhú)
- 觀音粉/观音粉
- 觀音素/观音素
- 觀音經/观音经
- 觀音草/观音草
- 觀音菊/观音菊
- 觀音菩薩/观音菩萨 (Guānyīn Púsà)
- 觀音蓮/观音莲
- 觀音衲/观音衲
- 觀音誕/观音诞 (Guānyīndàn)
- 角音
- 言音
- 訃音/讣音 (fùyīn)
- 託音/托音
- 訕音/讪音
- 訣音/诀音
- 訛音/讹音
- 詒音/诒音
- 詔音/诏音
- 話音/话音 (huàyīn)
- 試音/试音
- 誨音/诲音
- 語音/语音 (yǔyīn)
- 語音信箱/语音信箱 (yǔyīn xìnxiāng)
- 語音合成/语音合成
- 語音學/语音学 (yǔyīnxué)
- 語音郵件/语音邮件 (yǔyīn yóujiàn)
- 調音/调音 (tiáoyīn)
- 諧音/谐音 (xiéyīn)
- 譯音/译音 (yìyīn)
- 譯音符號/译音符号
- 讀音/读音 (dúyīn)
- 變徵之音/变征之音 (biànzhǐzhīyīn)
- 谷音
- 貳音/贰音
- 賞音/赏音
- 賽音/赛音
- 走音 (zǒuyīn)
- 起音
- 超音波 (chāoyīnbō)
- 超音速 (chāoyīnsù)
- 足音 (zúyīn)
- 足音空谷
- 足音跫然
- 路加福音 (Lùjiā Fúyīn)
- 跫然足音
- 跳音
- 跫音
- 車音/车音
- 輕脣音/轻唇音 (qīngchúnyīn)
- 輔音/辅音 (fǔyīn)
- 輕音樂/轻音乐 (qīngyīnyuè)
- 輝音/辉音
- 轉音/转音 (zhuǎnyīn)
- 送子觀音/送子观音
- 送氣音/送气音 (sòngqìyīn)
- 迴音壁/回音壁
- 逗音
- 通音 (tōngyīn)
- 連音/连音 (liányīn)
- 連音符/连音符
- 遐音
- 遁音
- 遏音
- 適音/适音
- 遺音/遗音
- 遺音餘韻/遗音余韵
- 還音/还音
- 邊擦音/边擦音 (biāncāyīn)
- 邊音/边音 (biānyīn)
- 邏輯重音/逻辑重音
- 邪音
- 邸音
- 鄉村音樂/乡村音乐 (xiāngcūn yīnyuè)
- 鄉音/乡音 (xiāngyīn)
- 鄭衛之音/郑卫之音 (zhèngwèizhīyīn)
- 鄭音/郑音
- 配音 (pèiyīn)
- 醜音/丑音
- 重唇音 (zhòngchúnyīn)
- 重脣音/重唇音 (zhòngchúnyīn)
- 重音 (zhòngyīn)
- 野音
- 金口玉音
- 金音
- 銅音/铜音
- 錄音/录音 (lùyīn)
- 錯音/错音
- 錄音室/录音室
- 錄音帶/录音带 (lùyīndài)
- 錄音機/录音机 (lùyīnjī)
- 錄音間/录音间
- 錄音電話/录音电话 (lùyīn diànhuà)
- 鎖骨觀音/锁骨观音
- 鐵觀音/铁观音 (tiěguānyīn)
- 鑾音/銮音
- 閃音/闪音 (shǎnyīn)
- 閉音節/闭音节 (bìyīnjié)
- 開口元音/开口元音
- 閏音/闰音
- 防音牆/防音墙
- 附點音符/附点音符 (fùdiǎnyīnfú)
- 降元音
- 陪音
- 隔音 (géyīn)
- 隔音室
- 隔音板
- 隔音牆/隔音墙
- 隔音符號/隔音符号 (géyīn fúhào)
- 隔音紙/隔音纸
- 隴頭音信/陇头音信
- 雁音
- 雅音
- 雙唇音/双唇音 (shuāngchúnyīn)
- 雙脣音/双唇音 (shuāngchúnyīn)
- 雜音/杂音 (záyīn)
- 雙音節/双音节 (shuāngyīnjié)
- 電子音樂/电子音乐 (diànzǐ yīnyuè)
- 雷射音響/雷射音响
- 電腦音樂/电脑音乐
- 電話錄音/电话录音
- 雷音
- 震音 (zhènyīn)
- 靈音/灵音
- 青林音樂/青林音乐
- 靜音/静音 (jìngyīn)
- 靡靡之音 (mǐmǐzhīyīn)
- 革音
- 鞉音
- 韲音
- 音伎
- 音位 (yīnwèi)
- 音位學/音位学 (yīnwèixué)
- 音使
- 音信 (yīnxìn)
- 音信杳然 (yīnxìnyǎorán)
- 音信杳無/音信杳无
- 音值 (yīnzhí)
- 音像 (yīnxiàng)
- 音像製品/音像制品
- 音儀/音仪
- 音兒/音儿
- 音切
- 音制
- 音勢/音势
- 音區/音区
- 音叉 (yīnchā)
- 音句
- 音吐
- 音名 (yīnmíng)
- 音呂/音吕
- 音和
- 音品
- 音問/音问
- 音問兩絕/音问两绝
- 音問杳然/音问杳然
- 音問相繼/音问相继
- 音均
- 音型
- 音域 (yīnyù)
- 音塵/音尘
- 音奏
- 音姿
- 音字
- 音學/音学
- 音學五書/音学五书
- 音學十書/音学十书
- 音官
- 音容 (yīnróng)
- 音容如在
- 音容宛在
- 音容淒斷/音容凄断
- 音容笑貌 (yīnróngxiàomào)
- 音帶/音带
- 音序
- 音強/音强
- 音形
- 音影
- 音律 (yīnlǜ)
- 音徽
- 音息
- 音感 (yīngǎn)
- 音意
- 音感作畫/音感作画
- 音技
- 音指
- 音效 (yīnxiào)
- 音效卡
- 音旨
- 音景
- 音曲
- 音書/音书
- 音柱 (yīnzhù)
- 音格
- 音栓
- 音標/音标 (yīnbiāo)
- 音樂/音乐 (yīnyuè)
- 音樂劇/音乐剧 (yīnyuèjù)
- 音樂卡/音乐卡
- 音樂家/音乐家 (yīnyuèjiā)
- 音樂廳/音乐厅 (yīnyuètīng)
- 音標文字/音标文字
- 音樂會/音乐会 (yīnyuèhuì)
- 音樂治療/音乐治疗 (yīnyuè zhìliáo)
- 音樂片/音乐片
- 音樂盒/音乐盒 (yīnyuèhé)
- 音樂站/音乐站
- 音樂節/音乐节
- 音樂臺/音乐台
- 音樂茶座/音乐茶座 (yīnyuè cházuò)
- 音樂週/音乐周
- 音樂鋸/音乐锯
- 音樂電鈴/音乐电铃
- 音正詞圓/音正词圆
- 音步 (yīnbù)
- 音氣/音气
- 音波 (yīnbō)
- 音準/音准
- 音爆
- 音片
- 音界號/音界号
- 音畫/音画
- 音痴 (yīnchī)
- 音監/音监
- 音盲
- 音碟機/音碟机
- 音程 (yīnchéng)
- 音稀信杳
- 音符 (yīnfú)
- 音節/音节 (yīnjié)
- 音節文字/音节文字 (yīnjié wénzì)
- 音箱 (yīnxiāng)
- 音籟/音籁
- 音系 (yīnxì)
- 音素 (yīnsù)
- 音素文字 (yīnsù wénzì)
- 音綴/音缀
- 音義/音义 (yīnyì)
- 音翰
- 音耗 (yīnhào)
- 音耗不絕/音耗不绝
- 音聞/音闻
- 音聲/音声 (yīnshēng)
- 音聲人/音声人
- 音聲如鐘/音声如钟
- 音聲子/音声子
- 音聲樹/音声树
- 音色 (yīnsè)
- 音華/音华
- 音訊/音讯 (yīnxùn)
- 音訓/音训 (yīnxùn)
- 音詞/音词
- 音誨/音诲
- 音語/音语
- 音調/音调 (yīndiào)
- 音謡/音谣
- 音謠/音谣
- 音譯/音译 (yīnyì)
- 音譯詞/音译词 (yīnyìcí)
- 音讀/音读 (yīndú)
- 音變/音变 (yīnbiàn)
- 音貺/音贶
- 音質/音质 (yīnzhì)
- 音軌/音轨 (yīnguǐ)
- 音辭/音辞
- 音速 (yīnsù)
- 音郵/音邮
- 音部記號/音部记号
- 音釋/音释
- 音重
- 音量 (yīnliàng)
- 音長/音长
- 音階/音阶 (yīnjiē)
- 音障
- 音韻/音韵 (yīnyùn)
- 音韻學/音韵学 (yīnyùnxué)
- 音韻闡微/音韵阐微
- 音響/音响 (yīnxiǎng)
- 音響學/音响学
- 音響效果/音响效果
- 音頻/音频 (yīnpín)
- 音驛/音驿
- 音高 (yīngāo)
- 響音/响音 (xiǎngyīn)
- 類音/类音
- 顧音/顾音
- 顫音/颤音 (chànyīn)
- 風音/风音
- 飛音/飞音
- 養音九皋/养音九皋
- 餘音/余音 (yúyīn)
- 餘音嫋嫋/余音袅袅
- 餘音繞梁/余音绕梁
- 馬可福音/马可福音 (Mǎkě Fúyīn)
- 馬太福音/马太福音 (Mǎtài Fúyīn)
- 騷音/骚音
- 驛音/驿音
- 高元音
- 高音 (gāoyīn)
- 鬧音音/闹音音
- 魔音傳腦/魔音传脑
- 魚籃觀音/鱼篮观音
- 鯨音/鲸音
- 鳥音/鸟音
- 鳳音/凤音
- 鴞音/鸮音
- 鴻音/鸿音
- 鵲音/鹊音
- 鶴音/鹤音
- 鷇音/𬆮音
- 鸞音/鸾音
- 鸞音鶴信/鸾音鹤信
- 黃犬音/黄犬音
- 黃鵠音/黄鹄音
- 黑人音樂/黑人音乐 (hēirén yīnyuè)
- 鼃音閏位/鼃音闰位
- 鼓音
- 鼻化元音 (bíhuà yuányīn)
- 鼻破裂音
- 鼻音 (bíyīn)
- 齏音/齑音
- 齒唇音/齿唇音 (chǐchúnyīn)
- 齒音/齿音 (chǐyīn)
References
[edit]- “音”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database)[2], 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
Japanese
[edit]| Shinjitai | 音 | |
| Kyūjitai [1][2] |
音󠄁 音+ 󠄁?(Adobe-Japan1) |

|
| 音󠄃 音+ 󠄃?(Hanyo-Denshi) (Moji_Joho) | ||
| The displayed kanji may be different from the image due to your environment. See here for details. | ||
Kanji
[edit]- sound
- timbre
- Short for 音楽 (ongaku): music
- speech (phonetics)
- Short for 字音 (jion): Chinese-derived reading of a kanji
- news, tidings
Readings
[edit]- Go-on: おん (on, Jōyō)←おん (on, historical)←おむ (omu, ancient)
- Kan-on: いん (in, Jōyō)←いん (in, historical)←いむ (imu, ancient)
- Kun: おと (oto, 音, Jōyō); と (to, 音); ね (ne, 音, Jōyō); たより (tayori, 音り)
- Nanori: お (o); とん (ton); なり (nari); ねね (nene); のん (non); ひびき (hibiki); りり (riri)
Compounds
[edit]- 音韻 (on'in)
- 音価 (onka)
- 音階 (onkai)
- 音楽 (ongaku, “music”)
- 音感 (onkan)
- 音義 (ongi)
- 音響 (onkyō, “sound”)
- 音曲 (onkyoku)
- 音訓 (onkun)
- 音耗 (onmō)
- 音叉 (onsa)
- 音子 (onshi, “phonon”)
- 音字 (onji)
- 音質 (onshitsu)
- 音色 (onshoku)
- 音信 (onshin)
- 音塵 (onjin)
- 音声 (onsei)
- 音制 (onsei)
- 音節 (onsetsu)
- 音素 (onso)
- 音息 (onsoku)
- 音速 (onsoku)
- 音痴 (onchi)
- 音注 (onchū)
- 音調 (onchō)
- 音程 (ontei)
- 音通 (ontsū)
- 音頭 (ondo)
- 音読 (ondoku)
- 音波 (onpa)
- 音標文字 (onpyōmoji)
- 音便 (onbin)
- 音符 (onpu)
- 音譜 (onpu)
- 音問 (onmon)
- 音訳 (on'yaku)
- 音律 (onritsu)
- 音量 (onryō)
- 観音 (kannon)
- 子音 (shīn), 子音 (shion, “consonant”)
- 震音 (shin'on, “tremolo”)
- 琵音 (bion): arpeggio
- 母音 (boin), 母音 (bōn, “vowel”)
- 漣音 (ren'on, “mordent”)
Etymology 1
[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 音 |
| おん Grade: 1 |
| on'yomi |
*/ʔiəm/ → /əmʉ/ → /omʉ/ → /oɴ/
From Middle Chinese 音 (MC 'im).
Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]- sound
- (linguistics) speech sound
- Short for 音読み (on'yomi): the Chinese-derived reading of a kanji
- (by extension) reading of a Chinese character outside the Japanese language; rime
- Short for 音楽 (ongaku): music
Derived terms
[edit]Etymology 2
[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 音 |
| おと Grade: 1 |
| kun'yomi |
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 音 |
| おっと Grade: 1 |
| kun'yomi |
⟨oto2⟩ → */otə/ → /oto/
From Old Japanese, from Proto-Japonic *ətə.
Appears in the late 1400s with the geminate pronunciation /otto/.[5] This reading is very rare, and appears to have fallen out of use.
Pronunciation
[edit](rare, obsolete)
Noun
[edit]- a sound
- when used with a "hear" verb, a rumor or fame (Can we verify(+) this sense?)
- news, tidings
- a reply, response
Usage notes
[edit]Oto is used for loud sounds and voices, as opposed to the ne reading.
Derived terms
[edit]Etymology 3
[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 音 |
| と Grade: 1 |
| kun'yomi |
⟨to2⟩ → */tə/ → /to/
The shift from oto, with the initial o being dropped.
The drop is likely due to haplology with the possessive particle の (no).
Noun
[edit]- sound; echo; voice
- , text here
- 可是能等能登抱吉和伎母賀吉西斯伎奴多母登乃久太利麻欲比伎尓家利 [Man'yōgana]
- 風の音の遠き我妹が着せし衣手本のくだりまよひ来にけり [Modern spelling]
- kaze no to no tōki wagimo ga kiseshi-kinu tamoto no kudari, mayoi-ki ni keri
- My dear wife, far away (as the sound of the wind), some threads of the sleeves of the kimono you made me wear have come to be worn and chafed![7]
- , text here
Derived terms
[edit]- 風の音の (kaze no to no, pillow word)
Etymology 4
[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 音 |
| ね Grade: 1 |
| kun'yomi |
| Alternative spelling |
|---|
| 哭 |
⟨ne2⟩ → */nəɨ/ → /ne/
From Old Japanese. First attested in the Kojiki of 712, with the phonetic spelling 泥.[8]
The original meaning appears to have been "a sound or cry, as made by an insect, bird, or beast".[8] The verb for making such a sound is 鳴く (naku, “to make a sound; to cry out”), cognate with 泣く (naku, “to cry, to weep”). It remains unclear if this noun ne ("sound") might be related to the verb naku ("to make a sound").
Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]Usage notes
[edit]Ne is used for relatively soft sounds and voices that appeals to human emotions, as opposed to the oto reading.
Derived terms
[edit]- 音色 (neiro, “timbre”)
- 泣く, 哭く (naku, “cry”)
- 空音 (sorane, “imitative cry”)
- 本音 (honne, “real intention; motive”)
Etymology 5
[edit]
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 音 |
| いん Grade: 1 |
| kan'on |
From Middle Chinese 音 (MC 'im).
The kan'on pronunciation, so likely a later borrowing.
Pronunciation
[edit]Affix
[edit]- (uncommon) Alternative form of 音 (on)
References
[edit]- ^ Haga, Gōtarō (1914) 漢和大辞書 [The Great Kanji-Japanese Dictionary] (in Japanese), Fourth edition, Tōkyō: Kōbunsha, , page 2305 (paper), page 1204 (digital)
- ^ Shōundō Henshūjo, editor (1927), 新漢和辞典 [The New Kanji-Japanese Dictionary] (in Japanese), Ōsaka: Shōundō, , page 1353 (paper), page 689 (digital)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Matsumura, Akira, editor (2006), 大辞林 [Daijirin] (in Japanese), Third edition, Tokyo: Sanseidō, →ISBN
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 NHK Broadcasting Culture Research Institute, editor (1998), NHK日本語発音アクセント辞典 [NHK Japanese Pronunciation Accent Dictionary] (in Japanese), Tokyo: NHK Publishing, Inc., →ISBN
- ^ Shōgaku Tosho (1988) 国語大辞典(新装版) [Unabridged Dictionary of Japanese (Revised Edition)] (in Japanese), Tōkyō: Shogakukan, →ISBN
- ^ Kindaichi, Kyōsuke et al., editors (1974), 新明解国語辞典 [Shin Meikai Kokugo Jiten] (in Japanese), Second edition, Tokyo: Sanseidō
- ^ Jan Lodewijk Pierson, Jr. (1964) The Makura-Kotoba of the Manyôśû, Leiden: Brill Archive, page 54
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 “音”, in 日本国語大辞典 [Nihon Kokugo Daijiten][1] (in Japanese), concise edition, Tokyo: Shogakukan, 2000
Korean
[edit]Etymology
[edit](This etymology is missing or incomplete. Please add to it, or discuss it at the Etymology scriptorium. Particularly: “Middle Korean readings, if any”)
Pronunciation
[edit]- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key): [ɯm]
- Phonetic hangul: [음]
Hanja
[edit]Synonyms
[edit]Compounds
[edit]Kunigami
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Etymology
[edit]From Proto-Ryukyuan *oto, from Proto-Japonic *ətə.
Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]音 (futū)
Okinawan
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]Etymology
[edit]From Proto-Ryukyuan *oto, from Proto-Japonic *ətə.
Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]音 (utu)
Old Korean
[edit]Phonogram
[edit]音 (*-m)
- A consonantal phonogram denoting coda consonant *-m
Tày
[edit]Adjective
[edit]音 (ăm)
- Nôm form of ăm (“dead at birth”).
- 𫰤蘆生𪦸音邊𱖨
- Mẻ rầư sinh lủc ăm vần vái
- Mothers who bear stillborns are immoral
References
[edit]- Lục Văn Pảo, Hoàng Tuấn Nam (2003) Hoàng Triều Ân, editor, Từ điển chữ Nôm Tày [A Dictionary of (chữ) Nôm Tày][3] (in Vietnamese), Hanoi: Nhà xuất bản Khoa học Xã hội
Vietnamese
[edit]Han character
[edit]音: Hán Nôm readings: âm, ậm, ơm
Compounds
[edit]Usage notes
[edit]- Chữ Nôm. The modern Vietnamese equivalent is âm.
References
[edit]Yaeyama
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Etymology
[edit]From Proto-Ryukyuan *oto, from Proto-Japonic *ətə.
Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]音 (utu)
Yonaguni
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Noun
[edit]音 (utu)
- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Kangxi Radicals block
- Han character radicals
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- Shuowen radicals
- Han ideograms
- Mandarin terms with audio links
- Cantonese terms with audio links
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Sichuanese lemmas
- Dungan lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Taishanese lemmas
- Gan lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Jin lemmas
- Northern Min lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Xiang lemmas
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese hanzi
- Mandarin hanzi
- Sichuanese hanzi
- Dungan hanzi
- Cantonese hanzi
- Taishanese hanzi
- Gan hanzi
- Hakka hanzi
- Jin hanzi
- Northern Min hanzi
- Eastern Min hanzi
- Hokkien hanzi
- Teochew hanzi
- Wu hanzi
- Xiang hanzi
- Middle Chinese hanzi
- Old Chinese hanzi
- Chinese nouns
- Mandarin nouns
- Sichuanese nouns
- Dungan nouns
- Cantonese nouns
- Taishanese nouns
- Gan nouns
- Hakka nouns
- Jin nouns
- Northern Min nouns
- Eastern Min nouns
- Hokkien nouns
- Teochew nouns
- Wu nouns
- Xiang nouns
- Middle Chinese nouns
- Old Chinese nouns
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese terms spelled with 音
- Mandarin terms with usage examples
- zh:Music
- Chinese nouns classified by 粒
- zh:Phonetics
- Intermediate Mandarin
- zh:Sound
- Japanese kanji
- Japanese first grade kanji
- Japanese kyōiku kanji
- Japanese jōyō kanji
- Japanese short forms
- Japanese autological terms
- Japanese kanji with goon reading おん
- Japanese kanji with historical goon reading おん
- Japanese kanji with ancient goon reading おむ
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading いん
- Japanese kanji with historical kan'on reading いん
- Japanese kanji with ancient kan'on reading いむ
- Japanese kanji with kun reading おと
- Japanese kanji with kun reading と
- Japanese kanji with kun reading ね
- Japanese kanji with kun reading たよ・り
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading お
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading とん
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading なり
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ねね
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading のん
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ひびき
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading りり
- Japanese terms spelled with 音 read as おん
- Japanese terms read with on'yomi
- Japanese terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Japanese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Japanese lemmas
- Japanese nouns
- Japanese terms with multiple readings
- Japanese terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Japanese terms written with one Han script character
- Japanese terms spelled with 音
- Japanese single-kanji terms
- ja:Linguistics
- Japanese terms spelled with 音 read as おと
- Japanese terms read with kun'yomi
- Japanese terms spelled with 音 read as おっと
- Japanese terms inherited from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms derived from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms inherited from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms derived from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms with usage examples
- Japanese terms spelled with 音 read as と
- Japanese terms spelled with 音 read as ね
- Japanese terms spelled with 音 read as いん
- Japanese terms read with kan'on
- Japanese affixes
- Japanese terms with uncommon senses
- ja:Sound
- Korean lemmas
- Korean hanja
- Korean hanja forms
- Hanja readings
- Kunigami kanji
- Kunigami first grade kanji
- Kunigami kyōiku kanji
- Kunigami jōyō kanji
- Kunigami kanji with kun reading ふと゚ぅー
- Kunigami terms inherited from Proto-Ryukyuan
- Kunigami terms derived from Proto-Ryukyuan
- Kunigami terms inherited from Proto-Japonic
- Kunigami terms derived from Proto-Japonic
- Kunigami terms with IPA pronunciation
- Kunigami lemmas
- Kunigami nouns
- Kunigami terms with multiple readings
- Kunigami terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Kunigami terms written with one Han script character
- Kunigami terms spelled with 音
- Kunigami single-kanji terms
- xug:Sound
- Okinawan kanji
- Okinawan first grade kanji
- Okinawan kyōiku kanji
- Okinawan jōyō kanji
- Okinawan kanji with kun reading うとぅ
- Okinawan terms inherited from Proto-Ryukyuan
- Okinawan terms derived from Proto-Ryukyuan
- Okinawan terms inherited from Proto-Japonic
- Okinawan terms derived from Proto-Japonic
- Okinawan terms with IPA pronunciation
- Okinawan lemmas
- Okinawan nouns
- Okinawan terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Okinawan terms written with one Han script character
- Okinawan terms spelled with 音
- Okinawan single-kanji terms
- ryu:Sound
- Old Korean phonograms
- Old Korean lemmas
- Tày lemmas
- Tày adjectives
- Tày Nôm forms
- Tày terms with usage examples
- Vietnamese lemmas
- Vietnamese Han characters
- Vietnamese Chữ Hán
- Yaeyama kanji
- Yaeyama first grade kanji
- Yaeyama kyōiku kanji
- Yaeyama jōyō kanji
- Yaeyama kanji with kun reading うとぅ
- Yaeyama terms inherited from Proto-Ryukyuan
- Yaeyama terms derived from Proto-Ryukyuan
- Yaeyama terms inherited from Proto-Japonic
- Yaeyama terms derived from Proto-Japonic
- Yaeyama terms with IPA pronunciation
- Yaeyama lemmas
- Yaeyama nouns
- Yaeyama terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Yaeyama terms written with one Han script character
- Yaeyama terms spelled with 音
- Yaeyama single-kanji terms
- rys:Sound
- Yonaguni kanji
- Yonaguni first grade kanji
- Yonaguni kyōiku kanji
- Yonaguni jōyō kanji
- Yonaguni kanji with kun reading うとぅ
- Yonaguni lemmas
- Yonaguni nouns
- Yonaguni terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Yonaguni terms written with one Han script character
- Yonaguni terms spelled with 音
- Yonaguni single-kanji terms
- CJKV radicals
- yoi:Sound

