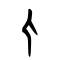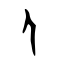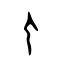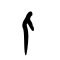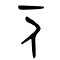人
 | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
Translingual
[edit]| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
Alternative forms
[edit]Han character
[edit]人 (Kangxi radical 9, 人+0, 2 strokes, cangjie input 人 (O), four-corner 80000, composition ⿸丿㇏)
- Kangxi radical #9, ⼈.
Derived characters
[edit]References
[edit]- Kangxi Dictionary: page 91, character 1
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 344
- Dae Jaweon: page 190, character 1
- Hanyu Da Zidian (first edition): volume 1, page 101, character 10
- Unihan data for U+4EBA
Chinese
[edit]Glyph origin
[edit]| Historical forms of the character 人 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Spring and Autumn | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Hanjian (compiled in Song) | Guwen Sishengyun (compiled in Song) | Jizhuan Guwen Yunhai (compiled in Song) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) | Libian (compiled in Qing) | Tang Stone Classics | Kangxi Dictionary (compiled in Qing) | |||||
| Bronze inscriptions | Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Bronze inscriptions | Chu slip and silk script | Qin slip script | Odd character | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts | Transcribed ancient scripts | Transcribed ancient scripts | Transcribed ancient scripts | Clerical script | Regular script | Ming typeface |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
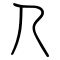
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
References:
Mostly from Richard Sears' Chinese Etymology site (authorisation),
| ||||||||||||||||
Pictogram (象形) – side view of a standing man, highlighting the arms and legs. Compare 大.
Etymology 1
[edit]| simp. and trad. |
人 | |
|---|---|---|
| alternative forms | ||
Sagart (1999) relates it to Tibetan ཉེན (nyen, “relative”), from ཉེ (nye, “near”) + nominalizing suffix -n; if so, from Proto-Sino-Tibetan *s-naːj ~ s-nej (“near”).
Schuessler (2007) proposes two etymologies:
- Same etymon as 仁 (OC *njin, “to be kind; to be good”), from Proto-Sino-Tibetan *s/k-niŋ (“heart; brain; mind”). The semantic association of 仁 with 人 was somewhat late, dated to Mencius's time; later on, 仁 would be usually interpreted as "humane, acting like a human being".
- Related to Proto-Mon-Khmer *ɲaʔ ~ *ɲah (“person”) with a nominalizing suffix -n, from the auto-ethnonym of a hostile, possibly Austroasiatic-speaking, eastern people, whom the Sinitic-speaking Shang referred to as 人方 (OC *njin paŋ).
Pronunciation
[edit]- Mandarin
- (Standard)
- (Chengdu, Sichuanese Pinyin): ren2
- (Xi'an, Guanzhong Pinyin): rén
- (Dungan, Cyrillic and Wiktionary): жын (řɨn, I)
- Cantonese
- Gan (Wiktionary): nyin4 / liin4
- Hakka
- Jin (Wiktionary): reng1
- Northern Min (KCR): nêng
- Eastern Min (BUC): ìng
- Southern Min
- Wu (Wugniu)
- Xiang (Changsha, Wiktionary): ren2
- Mandarin
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Hanyu Pinyin:
- Zhuyin: ㄖㄣˊ
- Tongyong Pinyin: rén
- Wade–Giles: jên2
- Yale: rén
- Gwoyeu Romatzyh: ren
- Palladius: жэнь (žɛnʹ)
- Sinological IPA (key): /ʐən³⁵/
- (Chengdu)
- Sichuanese Pinyin: ren2
- Scuanxua Ladinxua Xin Wenz: rhen
- Sinological IPA (key): /zən²¹/
- (Xi'an)
- Guanzhong Pinyin: rén
- Sinological IPA (key): /ʐẽ²⁴/
- (Dungan)
- Cyrillic and Wiktionary: жын (řɨn, I)
- Sinological IPA (key): /ʐəŋ²⁴/
- (Note: Dungan pronunciation is currently experimental and may be inaccurate.)
- (Standard Chinese)+
- Cantonese
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Jyutping: jan4 / jan4-2 / jan4-1
- Yale: yàhn / yán / yān
- Cantonese Pinyin: jan4 / jan4-2 / jan4-1
- Guangdong Romanization: yen4 / yen4-2 / yen4-1
- Sinological IPA (key): /jɐn²¹/, /jɐn²¹⁻³⁵/, /jɐn²¹⁻⁵⁵/
- (Taishanese, Taicheng)
- Wiktionary: ngin3
- Sinological IPA (key): /ᵑɡin²²/
- (Standard Cantonese, Guangzhou–Hong Kong)
- Gan
- (Nanchang)
- Wiktionary: nyin4 / liin4
- Sinological IPA (key): /n̠ʲin³⁵/, /lɨn³⁵/
- (Nanchang)
- nyin4 - vernacular;
- liin4 - literary.
- Hakka
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: ngìn
- Hakka Romanization System: nginˇ
- Hagfa Pinyim: ngin2
- Sinological IPA: /ŋin¹¹/
- (Meixian)
- (Sixian, incl. Miaoli and Meinong)
- Jin
- (Taiyuan)+
- Wiktionary: reng1
- Sinological IPA (old-style): /ʐə̃ŋ¹¹/
- (Taiyuan)+
- Northern Min
- (Jian'ou)
- Kienning Colloquial Romanized: nêng
- Sinological IPA (key): /neiŋ³³/
- (Jian'ou)
- Eastern Min
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: ìng
- Sinological IPA (key): /iŋ⁵³/
- (Fuzhou)
- Southern Min
- (Hokkien: Zhangzhou, Kaohsiung)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: jîn
- Tâi-lô: jîn
- Phofsit Daibuun: jiin
- IPA (Kaohsiung): /zin²³/
- IPA (Zhangzhou): /d͡zin¹³/
- (Hokkien: Xiamen, Quanzhou, Jinjiang, Taipei, Singapore)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: lîn
- Tâi-lô: lîn
- Phofsit Daibuun: liin
- IPA (Xiamen, Quanzhou, Jinjiang, Taipei, Singapore): /lin²⁴/
- (Teochew)
- Peng'im: ring5 / rêng5
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī-like: jîng / jêng
- Sinological IPA (key): /d͡ziŋ⁵⁵/, /d͡zeŋ⁵⁵/
- (Hokkien: Zhangzhou, Kaohsiung)
- rêng5 - Jieyang;
- ring5 - other places.
- Wu
- (Northern: Shanghai)
- Wugniu: 6gnin
- MiniDict: nyin去
- Wiktionary Romanisation (Shanghai): 3nyin
- Sinological IPA (Shanghai): /n̠ʲin²³/
- (Northern: Jiading, Songjiang, Chongming, Suzhou, Changzhou, Jiaxing, Tongxiang, Haining, Haiyan, Hangzhou, Shaoxing, Ningbo)
- Wugniu: 2gnin
- MiniDict: nyin平
- Sinological IPA (Jiading): /n̠ʲiŋ³¹/
- Sinological IPA (Songjiang): /n̠ʲiŋ³¹/
- Sinological IPA (Chongming): /ɦn̠ʲin²⁴/
- Sinological IPA (Suzhou): /n̠ʲin²²³/
- Sinological IPA (Changzhou): /n̠ʲiŋ¹³/
- Sinological IPA (Jiaxing): /n̠ʲin³¹/
- Sinological IPA (Tongxiang): /n̠ʲin²²/
- Sinological IPA (Haining): /n̠ʲin¹¹³/
- Sinological IPA (Haiyan): /n̠ʲiən³¹/
- Sinological IPA (Hangzhou): /n̠ʲin²³/
- Sinological IPA (Shaoxing): /n̠ʲiŋ²³¹/
- Sinological IPA (Ningbo): /n̠ʲiŋ³¹³/
- (Northern: Shanghai)
- Wugniu: 6zen
- MiniDict: zen去
- Wiktionary Romanisation (Shanghai): 3zen
- Sinological IPA (Shanghai): /zən²³/
- (Northern: Jiading, Songjiang, Chongming, Suzhou, Changzhou, Jiaxing, Tongxiang, Haining, Haiyan, Hangzhou)
- Wugniu: 2zen
- MiniDict: zen平
- Sinological IPA (Jiading): /zəŋ³¹/
- Sinological IPA (Songjiang): /zəŋ³¹/
- Sinological IPA (Chongming): /szən²⁴/
- Sinological IPA (Suzhou): /zən²²³/
- Sinological IPA (Changzhou): /zəŋ¹³/
- Sinological IPA (Jiaxing): /zən³¹/
- Sinological IPA (Tongxiang): /zən²²/
- Sinological IPA (Haining): /zən¹¹³/
- Sinological IPA (Haiyan): /zən³¹/
- Sinological IPA (Hangzhou): /zen²³/
- (Northern: Shaoxing)
- (Northern: Ningbo)
- (Jinhua)
- (Northern: Shanghai)
- gnin - colloquial;
- zen, 2zeen (Shaoxing), 2zyun (Ningbo) - literary;
- 2gnin (Hangzhou) - younger speakers only, influenced by other Wu lects.
- Xiang
- (Changsha)
- Wiktionary: ren2
- Sinological IPA (key): /ʐən¹³/
- (Changsha)
- Dialectal data
| Variety | Location | 人 |
|---|---|---|
| Mandarin | Beijing | /ʐən³⁵/ |
| Harbin | /ʐən²⁴/ /in²⁴/ | |
| Tianjin | /in⁴⁵/ /ʐən⁴⁵/ | |
| Jinan | /ʐẽ⁴²/ | |
| Qingdao | /iə̃⁴²/ | |
| Zhengzhou | /ʐən⁴²/ | |
| Xi'an | /ʐẽ²⁴/ | |
| Xining | /ʐə̃²¹³/ | |
| Yinchuan | /ʐəŋ⁵³/ | |
| Lanzhou | /ʐə̃n⁵³/ | |
| Ürümqi | /ʐɤŋ⁵¹/ | |
| Wuhan | /nən²¹³/ | |
| Chengdu | /zən³¹/ | |
| Guiyang | /zen²¹/ | |
| Kunming | /ʐə̃³¹/ | |
| Nanjing | /ʐən²⁴/ | |
| Hefei | /ʐən⁵⁵/ | |
| Jin | Taiyuan | /zəŋ¹¹/ |
| Pingyao | /ʐəŋ¹³/ | |
| Hohhot | /ʐə̃ŋ³¹/ | |
| Wu | Shanghai | /ȵiŋ²³/ /zəŋ²³/ |
| Suzhou | /zən¹³/ /ȵin¹³/ | |
| Hangzhou | /zen²¹³/ | |
| Wenzhou | /zaŋ³¹/ 文讀 /ȵaŋ³¹/ 白讀 /naŋ³¹/ 訓讀 | |
| Hui | Shexian | /iʌ̃⁴⁴/ /niʌ̃⁴⁴/ |
| Tunxi | /ian⁴⁴/ | |
| Xiang | Changsha | /ʐən¹³/ |
| Xiangtan | /in¹²/ | |
| Gan | Nanchang | /ȵin⁴⁵/ /lɨn⁴⁵/ ~參 |
| Hakka | Meixian | /ŋin¹¹/ |
| Taoyuan | /ŋin¹¹/ | |
| Cantonese | Guangzhou | /jɐn²¹/ |
| Nanning | /jɐn²¹/ | |
| Hong Kong | /jɐn²¹/ | |
| Min | Xiamen (Hokkien) | /lin³⁵/ |
| Fuzhou (Eastern Min) | /iŋ⁵³/ | |
| Jian'ou (Northern Min) | /neiŋ³³/ | |
| Shantou (Teochew) | /ziŋ⁵⁵/ /naŋ⁵⁵/ 訓讀 | |
| Haikou (Hainanese) | /zin³¹/ /naŋ³¹/ 訓儂 |
- Middle Chinese: nyin
- Old Chinese
- (Baxter–Sagart): /*ni[ŋ]/
- (Zhengzhang): /*njin/
Definitions
[edit]人
- man; person; people (Classifier: 個/个 m c; 隻/只 h)
- 人類/人类 ― rénlèi ― humans
- 那人是誰?/那人是谁? ― Nà rén shì shéi? ― Who is that person?
- 有人敲門了。/有人敲门了。 ― Yǒurén qiāomén le. ― Someone knocked on the door.
-
- 無論過去抑如今 無論海水有外深 我的身邊總有天地人 [Taiwanese Hokkien, trad.]
- bô-lūn kòe-khì ia̍h jû-kim, bô-lūn hái-chúi ū gōa chhim, góa ê sin-piⁿ chóng ū thian tē jîn [Pe̍h-ōe-jī]
- No matter in the past or the present, no matter how deep the ocean is, I always have the heavens, the earth, and people by my side.
无论过去抑如今 无论海水有外深 我的身边总有天地人 [Taiwanese Hokkien, simp.]
- a person associated with a particular identity or trait; -er
- body
- everybody; everyone
- other people; others
- physical, psychological or moral quality or condition; character; personality (Classifier: 份 c; 個/个 c)
- manpower; worker; employee
- talent; person of talent
- (obsolete) common people; commoner
- 皇天上帝,后土神祇,眷顧降命,屬秀黎元,為人父母,秀不敢當。 [Literary Chinese, trad.]
- From: The Book of the Later Han, circa 5th century CE
- Huángtiān shàngdì, hòutǔ shénqí, juàngù jiàngmìng, shǔ Xiù líyuán, wéi rén fùmǔ, Xiù bùgǎn dāng. [Pinyin]
- (please add an English translation of this quotation)
皇天上帝,后土神祇,眷顾降命,属秀黎元,为人父母,秀不敢当。 [Literary Chinese, simp.]
- adult; grown-up
- artificial; man-made
- (fantasy, mythology) were- (indicates a person who changes shape into an animal)
- (Cantonese) used as a dummy pronoun; someone; others
- (Zhao'an Hakka) pluralizes a personal pronoun
- 𠊎人、你人、佢人 [Zhao'an Hakka, trad. and simp.]
- ngai` ngin`, hen` ngin`, gui` ngin` [Taiwanese Hakka Romanization System]
- we, you all, they
- (obsolete) sexual intercourse
- (obsolete) company; companion; friend
- (obsolete) human affairs; ways of the world
- (obsolete) mortal world; earthly word
- (obsolete) Alternative form of 仁 (rén, “kernel”)
- (obsolete) Alternative form of 仁 (rén, “charity”)
- (obsolete) Alternative form of 仁 (rén, “loving; kind”)
- (Beijing Mandarin) Lenition of 人家 (rénjia).
- (Taishanese) paternal grandmother
- a surname
Synonyms
[edit]Compounds
[edit]- 一人 (yīrén)
- 一人不敵眾人智/一人不敌众人智
- 一人之交
- 一人班
- 一家人 (yījiārén)
- 一樣米飼百樣人/一样米饲百样人
- 一行人
- 一表人才 (yībiǎoréncái)
- 一表人物
- 一語中人/一语中人
- 一路人 (yīlùrén)
- 一顧傾人/一顾倾人
- 一鳴驚人/一鸣惊人 (yīmíngjīngrén)
- 下人 (xiàrén)
- 上人
- 丈人
- 上人兒/上人儿
- 丈人峰
- 三人成虎 (sānrénchénghǔ)
- 三人行 (sānrénxíng)
- 丈人行
- 上大人
- 三明治人
- 下江人
- 上洞人
- 下路人
- 下里巴人 (xiàlǐbārén)
- 上門怪人/上门怪人
- 下頭人/下头人
- 不乏其人 (bùfáqírén)
- 不人道 (bùréndào)
- 不以人齒/不以人齿
- 不像人樣/不像人样
- 不具之人
- 不受苦中苦,難為人上人/不受苦中苦,难为人上人
- 不吃苦中苦,難為人上人/不吃苦中苦,难为人上人
- 不因人熱/不因人热
- 不在人間/不在人间
- 不容人
- 不得人心 (bùdérénxīn)
- 不成人
- 不敢後人/不敢后人
- 不是人
- 不是別人/不是别人
- 不求人 (bùqiúrén)
- 不為人下/不为人下
- 不為人用/不为人用
- 不甘後人/不甘后人 (bùgānhòurén)
- 不由人
- 不當人/不当人
- 不當人子/不当人子
- 不省人事 (bùxǐngrénshì)
- 不知人事
- 不良人 (bùliángrén)
- 不著人/不着人
- 不落人後/不落人后
- 不見人影/不见人影
- 不認人/不认人
- 不近人情 (bùjìn-rénqíng)
- 不逮人倫/不逮人伦
- 不醒人事 (bùxǐngrénshì)
- 不食人間煙火/不食人间烟火 (bù shí rénjiān yānhuǒ)
- 世人 (shìrén)
- 世態人情/世态人情
- 世海他人
- 世道人心 (shìdàorénxīn)
- 世道人情
- 丟人/丢人 (diūrén)
- 丟人現眼/丢人现眼 (diūrénxiànyǎn)
- 中人 (zhōngrén)
- 中心人物
- 中書舍人/中书舍人
- 中華人民共和國/中华人民共和国 (Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó)
- 中貴人/中贵人
- 中間人/中间人 (zhōngjiānrén)
- 中饋乏人/中馈乏人
- 丹麥人/丹麦人 (dānmàirén)
- 主人 (zhǔrén)
- 主人公 (zhǔréngōng)
- 主人婆
- 主人翁 (zhǔrénwēng)
- 主婚人
- 主持人 (zhǔchírén)
- 乏人
- 乏人問津/乏人问津 (fárénwènjīn)
- 乖人
- 乘人不備/乘人不备
- 乘人之危 (chéngrénzhīwēi)
- 乘人之厄
- 乞人 (qǐrén)
- 亂世佳人/乱世佳人
- 予一人 (yúyīrén)
- 予人口實/予人口实
- 事在人為/事在人为 (shìzàirénwéi)
- 二人臺/二人台 (èrréntái)
- 二人轉/二人转
- 二八佳人 (èrbājiārén)
- 二夫人
- 二形人
- 亞洲鐵人/亚洲铁人
- 亡人 (wángrén)
- 亡人自存
- 亮眼人
- 人一己百
- 人丁 (réndīng)
- 人上人 (rénshàngrén)
- 人不像人,鬼不像鬼 (rén bù xiàng rén, guǐ bù xiàng guǐ)
- 人不可貌相 (rén bùkě màoxiàng)
- 人不得外財不富/人不得外财不富
- 人不為己,天誅地滅/人不为己,天诛地灭 (rén bù wèi jǐ, tiān zhū dì miè)
- 人不聊生
- 人不自安
- 人世 (rénshì)
- 人中 (rénzhōng)
- 人中之龍/人中之龙 (rénzhōngzhīlóng)
- 人中獅子/人中狮子 (rén zhōng shīzi)
- 人中豪傑/人中豪杰 (rénzhōngháojié)
- 人中騏驥/人中骐骥
- 人中龍/人中龙
- 人中龍虎/人中龙虎
- 人主 (rénzhǔ)
- 人之常情 (rénzhīchángqíng)
- 人之患在好為人師/人之患在好为人师 (rén zhī huàn zài hàowéirénshī)
- 人事 (rénshì)
- 人事不省
- 人事不知
- 人事代謝/人事代谢
- 人事全非
- 人事管理
- 人事莫定
- 人事行政
- 人云亦云 (rényúnyìyún)
- 人亡家破
- 人亡政息 (rénwángzhèngxī)
- 人亡物在
- 人人 (rénrén)
- 人人稱快/人人称快
- 人人自危 (rénrénzìwēi)
- 人仰馬翻/人仰马翻 (rényǎngmǎfān)
- 人來人往/人来人往
- 人來客去/人来客去
- 人來客往/人来客往
- 人來瘋/人来疯 (rénláifēng)
- 人保 (rénbǎo)
- 人們/人们 (rénmen)
- 人倫/人伦 (rénlún)
- 人傑/人杰 (rénjié)
- 人傑地靈/人杰地灵 (rénjiédìlíng)
- 人像 (rénxiàng)
- 人兒/人儿
- 人前人後/人前人后
- 人力 (rénlì)
- 人力回天 (rénlìhuítiān)
- 人力資源/人力资源 (rénlì zīyuán)
- 人力車/人力车 (rénlìchē)
- 人力銀行/人力银行 (rénlì yínháng)
- 人勝節/人胜节
- 人勿可貌相
- 人千人萬/人千人万
- 人去樓空/人去楼空
- 人參/人参 (rénshēn)
- 人參吃飽了/人参吃饱了
- 人參果/人参果
- 人叢/人丛 (réncóng)
- 人口 (rénkǒu)
- 人口分布
- 人口問題/人口问题
- 人口密度 (rénkǒu mìdù)
- 人口政策
- 人口普查 (rénkǒu pǔchá)
- 人口爆炸 (rénkǒu bàozhà)
- 人口結構/人口结构 (rénkǒu jiégòu)
- 人口老化
- 人口販子/人口贩子
- 人口轉型/人口转型
- 人口過剩/人口过剩 (rénkǒu guòshèng)
- 人名 (rénmíng)
- 人各有志 (rén gè yǒuzhì)
- 人同此心
- 人君 (rénjūn)
- 人和
- 人命 (rénmìng)
- 人味兒/人味儿
- 人命危淺/人命危浅 (rénmìngwēiqiǎn)
- 人命關天/人命关天 (rénmìngguāntiān)
- 人品 (rénpǐn)
- 人員/人员 (rényuán)
- 人善得人欺,馬善得人騎/人善得人欺,马善得人骑 (rén shàn dé rén qī, mǎ shàn dé rén qí)
- 人喊馬嘶/人喊马嘶
- 人因工程
- 人困馬乏/人困马乏 (rénkùn-mǎfá)
- 人地 (réndì)
- 人地兩疏/人地两疏
- 人地生疏 (réndìshēngshū)
- 人地相宜
- 人境
- 人士 (rénshì)
- 人壽/人寿 (rénshòu)
- 人壽保險/人寿保险 (rénshòu bǎoxiǎn)
- 人壽年豐/人寿年丰 (rénshòuniánfēng)
- 人外無詩/人外无诗
- 人多勢眾/人多势众 (rénduōshìzhòng)
- 人多口雜/人多口杂 (rénduōkǒuzá)
- 人多嘴雜/人多嘴杂 (rénduōzuǐzá)
- 人多好辦事/人多好办事 (rénduōhǎobànshì)
- 人多成王
- 人多手亂/人多手乱
- 人多手腳亂/人多手脚乱 (rénduōshǒujiǎoluàn)
- 人多手雜/人多手杂
- 人大 (Réndà)
- 人大心大
- 人天
- 人夫 (rénfū)
- 人奶 (rénnǎi)
- 人如其名 (rénrúqímíng)
- 人妖 (rényāo)
- 人子 (rénzǐ)
- 人孔 (rénkǒng)
- 人存政舉/人存政举
- 人孤勢單/人孤势单
- 人定
- 人定勝天/人定胜天 (réndìngshèngtiān)
- 人客 (rénkè)
- 人家
- 人寰 (rénhuán)
- 人小鬼大
- 人山人海 (rénshānrénhǎi)
- 人工 (réngōng)
- 人工免疫
- 人工冬眠
- 人工受孕 (réngōng shòuyùn)
- 人工受精 (réngōng shòujīng)
- 人工呼吸 (réngōng hūxī)
- 人工島/人工岛 (réngōngdǎo)
- 人工心臟/人工心脏
- 人工成本
- 人工智慧 (réngōng zhìhuì)
- 人工植牙
- 人工氣胸/人工气胸
- 人工氣腹/人工气腹
- 人工流產/人工流产 (réngōng liúchǎn)
- 人工海鹽/人工海盐
- 人工繁殖
- 人工色素
- 人工蝸牛/人工蜗牛
- 人工血液
- 人工閱卷/人工阅卷
- 人工降雨 (réngōng jiàngyǔ)
- 人工養殖/人工养殖
- 人工魚礁/人工鱼礁
- 人己一視/人己一视
- 人師/人师 (rénshī)
- 人強馬壯/人强马壮 (rénqiángmǎzhuàng)
- 人彘
- 人形 (rénxíng)
- 人影 (rényǐng)
- 人影兒/人影儿 (rényǐngr)
- 人從/人从 (réncóng)
- 人微權輕/人微权轻
- 人微言輕/人微言轻 (rénwēiyánqīng)
- 人心 (rénxīn)
- 人心不古 (rénxīnbùgǔ)
- 人心叵測/人心叵测 (rénxīnpǒcè)
- 人心向背 (rénxīnxiàngbèi)
- 人心大快
- 人心如面
- 人心悄悄
- 人心惟危
- 人心惶惶 (rénxīnhuánghuáng)
- 人心所向 (rénxīnsuǒxiàng)
- 人心所歸/人心所归
- 人心果 (rénxīnguǒ)
- 人心渙散/人心涣散
- 人心渙漓/人心涣漓
- 人心皇皇
- 人心莫測/人心莫测
- 人心隔肚皮 (rénxīn gé dùpí)
- 人心難測/人心难测
- 人必自侮而後人侮之/人必自侮而后人侮之 (rén bì zìwǔ érhòu rén wǔ zhī)
- 人必自重而後人重之/人必自重而后人重之 (rén bì zìzhòng érhòu rén zhòng zhī)
- 人性 (rénxìng)
- 人急智生
- 人性枷鎖/人性枷锁
- 人怨神怒
- 人性管理
- 人急計生/人急计生
- 人情 (rénqíng)
- 人情世故 (rénqíngshìgù)
- 人情之常 (rénqíngzhīcháng)
- 人情冷暖 (rénqínglěngnuǎn)
- 人情味 (rénqíngwèi)
- 人情洶洶/人情汹汹
- 人情練達/人情练达 (rénqíngliàndá)
- 人情貨/人情货
- 人我是非
- 人戶/人户
- 人才 (réncái)
- 人手 (rénshǒu)
- 人手一冊/人手一册
- 人才出眾/人才出众
- 人才外流 (réncái wàiliú)
- 人才庫/人才库 (réncáikù)
- 人才濟濟/人才济济 (réncáijǐjǐ)
- 人才輩出/人才辈出 (réncáibèichū)
- 人才難得/人才难得
- 人扶人興/人扶人兴
- 人持各見/人持各见
- 人數/人数 (rénshù)
- 人文 (rénwén)
- 人文主義/人文主义 (rénwén zhǔyì)
- 人文教育
- 人文景觀/人文景观 (rénwén jǐngguān)
- 人文科學/人文科学 (rénwén kēxué)
- 人文薈萃/人文荟萃
- 人日 (rénrì)
- 人時/人时
- 人有三急 (rényǒusānjí)
- 人望 (rénwàng)
- 人本主義/人本主义 (rénběn zhǔyì)
- 人本說/人本说
- 人本論/人本论
- 人柳
- 人格 (réngé)
- 人格分裂 (réngé fēnliè)
- 人格化 (réngéhuà)
- 人格教育
- 人格權/人格权 (réngéquán)
- 人格測驗/人格测验
- 人梯
- 人棄我取/人弃我取
- 人樣/人样
- 人模人樣/人模人样
- 人樣兒/人样儿
- 人樣子/人样子
- 人模狗樣/人模狗样 (rénmógǒuyàng)
- 人機介面/人机介面
- 人權/人权 (rénquán)
- 人權宣言/人权宣言 (Rénquán Xuānyán)
- 人權運動/人权运动
- 人次 (réncì)
- 人欲 (rényù)
- 人欲橫流/人欲横流
- 人歡馬叫/人欢马叫 (rénhuānmǎjiào)
- 人死留名
- 人殊意異/人殊意异 (rén shū yì yì)
- 人比人,氣死人/人比人,气死人 (rén bǐ rén, qì sǐ rén)
- 人氏 (rénshì)
- 人民 (rénmín)
- 人民公社 (rénmín gōngshè)
- 人民團體/人民团体 (rénmín tuántǐ)
- 人民幣/人民币 (rénmínbì)
- 人民戰爭/人民战争 (rénmín zhànzhēng)
- 人民政府 (rénmín zhèngfǔ)
- 人民日報/人民日报
- 人氣/人气 (rénqì)
- 人氣指標/人气指标
- 人治 (rénzhì)
- 人海 (rénhǎi)
- 人海戰術/人海战术 (rénhǎi zhànshù)
- 人浮於事/人浮于事 (rénfúyúshì)
- 人浮於食/人浮于食
- 人渣 (rénzhā)
- 人溺己溺
- 人滿/人满
- 人滿為患/人满为患 (rénmǎnwéihuàn)
- 人潮 (réncháo)
- 人為/人为 (rénwéi)
- 人為財死,鳥為食亡/人为财死,鸟为食亡 (rén wèi cái sǐ, niǎo wèi shí wáng)
- 人無完人/人无完人 (rén wú wánrén)
- 人無橫財不富/人无横财不富
- 人無遠慮,必有近憂/人无远虑,必有近忧 (rén wú yuǎnlǜ, bì yǒu jìnyōu)
- 人煙/人烟 (rényān)
- 人煙浩穰/人烟浩穰 (rényānhàoráng)
- 人煙湊集/人烟凑集 (rényāncòují)
- 人煙稀少/人烟稀少 (rényānxīshǎo)
- 人煙稠密/人烟稠密 (rényānchóumì)
- 人煙輻輳/人烟辐辏 (rényānfúcòu)
- 人熊 (rénxióng)
- 人爵
- 人父 (rénfù)
- 人牙兒/人牙儿
- 人牧
- 人物 (rénwù)
- 人物字號/人物字号
- 人物畫/人物画 (rénwùhuà)
- 人物軒昂/人物轩昂
- 人物闐咽/人物阗咽
- 人犯 (rénfàn)
- 人猿
- 人猿泰山
- 人猿科
- 人獸交/人兽交 (rénshòujiāo)
- 人琴俱亡
- 人琴俱杳
- 人瑞 (rénruì)
- 人生 (rénshēng)
- 人生在世
- 人生如夢/人生如梦 (rénshēngrúmèng)
- 人生如寄
- 人生如戲/人生如戏
- 人生如萍
- 人生朝露
- 人生無常/人生无常
- 人生觀/人生观 (rénshēngguān)
- 人生路不熟 (rénshēnglùbùshú)
- 人生路勿熟
- 人畜 (rénchù)
- 人百其身
- 人皇
- 人盡其才/人尽其才
- 人盡可夫/人尽可夫 (rénjìnkěfū)
- 人盡皆知/人尽皆知 (rénjìnjiēzhī)
- 人相學/人相学
- 人眾勝天/人众胜天
- 人神 (rénshén)
- 人神共憤/人神共愤 (rénshéngòngfèn)
- 人神同憤/人神同愤
- 人祭 (rénjì)
- 人禍/人祸 (rénhuò)
- 人稠物穰
- 人種/人种 (rénzhǒng)
- 人稱/人称 (rénchēng)
- 人窩子/人窝子
- 人窮志氣短/人穷志气短
- 人窮志短/人穷志短 (rénqióngzhìduǎn)
- 人窮智短/人穷智短
- 人立
- 人籟/人籁
- 人紀/人纪
- 人約黃昏/人约黄昏
- 人給家足/人给家足
- 人緣/人缘 (rényuán)
- 人群 (rénqún)
- 人義水甜/人义水甜
- 人老珠黃/人老珠黄
- 人聲/人声 (rénshēng)
- 人聲鼎沸/人声鼎沸 (rénshēngdǐngfèi)
- 人肉市場/人肉市场 (rénròu shìchǎng)
- 人脈/人脉 (rénmài)
- 人臣 (rénchén)
- 人自為戰/人自为战
- 人與鼠/人与鼠
- 人莫予毒 (rénmòyúdú)
- 人蛇 (rénshé)
- 人行
- 人行道 (rénxíngdào)
- 人見人愛/人见人爱 (rénjiànrén'ài)
- 人言 (rényán)
- 人言可畏 (rényánkěwèi)
- 人言籍籍
- 人言鑿鑿/人言凿凿
- 人語馬嘶/人语马嘶
- 人謀/人谋
- 人謀不臧/人谋不臧
- 人證/人证 (rénzhèng)
- 人財兩失/人财两失 (réncáiliǎngshī)
- 人財兩空/人财两空 (réncáiliǎngkōng)
- 人販子/人贩子 (rénfànzi)
- 人貧智短/人贫智短
- 人質/人质 (rénzhì)
- 人贓俱獲/人赃俱获 (rénzāngjùhuò)
- 人跡/人迹 (rénjì)
- 人跡杳然/人迹杳然
- 人跡罕至/人迹罕至 (rénjìhǎnzhì)
- 人身 (rénshēn)
- 人身保險/人身保险 (rénshēn bǎoxiǎn)
- 人身自由 (rénshēn zìyóu)
- 人造 (rénzào)
- 人造纖維/人造纤维
- 人造花
- 人造衛星/人造卫星 (rénzào wèixīng)
- 人造雨
- 人道 (réndào)
- 人道主義/人道主义 (réndào zhǔyì)
- 人道教育
- 人選/人选 (rénxuǎn)
- 人鏡/人镜
- 人鏈/人链 (rénliàn)
- 人鑑/人鉴
- 人間/人间 (rénjiān)
- 人間仙境/人间仙境
- 人間冷暖/人间冷暖
- 人間喜劇/人间喜剧
- 人間地獄/人间地狱 (rénjiān dìyù)
- 人間天上/人间天上 (rénjiān tiānshàng)
- 人間煙火/人间烟火
- 人間詞話/人间词话
- 人際/人际 (rénjì)
- 人際傳播/人际传播
- 人際關係/人际关系 (rénjìguānxì)
- 人離家散/人离家散
- 人離鄉賤/人离乡贱 (rénlíxiāngjiàn)
- 人非人
- 人非木石
- 人非物換/人非物换
- 人面 (rénmiàn)
- 人面上
- 人面桃花 (rénmiàntáohuā)
- 人面獸心/人面兽心 (rénmiànshòuxīn)
- 人頭/人头 (réntóu)
- 人頭保/人头保
- 人頭兒/人头儿
- 人頭帳目/人头帐目
- 人頭戶/人头户
- 人頭支票/人头支票
- 人頭畜鳴/人头畜鸣
- 人頭稅/人头税 (réntóushuì)
- 人頭落地/人头落地
- 人類/人类 (rénlèi)
- 人類學/人类学 (rénlèixué)
- 人飢己飢/人饥己饥
- 人馬/人马 (rénmǎ)
- 人馬座/人马座 (Rénmǎzuò)
- 人體/人体 (réntǐ)
- 人體彩繪/人体彩绘 (réntǐ cǎihuì)
- 人體計測/人体计测 (réntǐ jìcè)
- 人高馬大/人高马大 (réngāomǎdà)
- 人鬼殊途
- 人魚/人鱼 (rényú)
- 仁人 (rénrén)
- 今人 (jīnrén)
- 仇人 (chóurén)
- 仁人君子 (rénrénjūnzǐ)
- 仁人志士 (rénrénzhìshì)
- 介紹人/介绍人 (jièshàorén)
- 令人 (lìngrén)
- 他人 (tārén)
- 仙人 (xiānrén)
- 令人不齒/令人不齿
- 令人切齒/令人切齿
- 代人受過/代人受过
- 以人廢言/以人废言 (yǐrénfèiyán)
- 令人心寒
- 令人意外
- 令人扼腕
- 仙人拳
- 代人捉刀
- 仙人掌 (xiānrénzhǎng)
- 令人捧腹
- 仙人擔/仙人担 (xiānréndàn)
- 仙人放屁
- 仙人渡 (Xiānréndù)
- 令人激賞/令人激赏
- 以人為本/以人为本 (yǐrénwéiběn)
- 以人為鑑/以人为鉴
- 令人矚目/令人瞩目
- 令人神往
- 令人絕倒/令人绝倒
- 仙人跳 (xiānréntiào)
- 令人髮指/令人发指 (lìngrénfàzhǐ)
- 令人齒冷/令人齿冷
- 以力服人
- 仗勢凌人
- 仗勢欺人/仗势欺人 (zhàngshìqīrén)
- 仙女座人 (xiānnǚzuòrén)
- 以容取人
- 令尊大人
- 以己度人 (yǐjǐduórén)
- 以德服人 (yǐdéfúrén)
- 付款人 (fùkuǎnrén)
- 代理人 (dàilǐrén)
- 以理服人 (yǐlǐfúrén)
- 代言人 (dàiyánrén)
- 以言取人
- 以貌取人 (yǐmàoqǔrén)
- 伊人 (yīrén)
- 任人
- 任人唯親/任人唯亲 (rènrénwéiqīn)
- 任人唯賢/任人唯贤 (rènrénwéixián)
- 任人宰割 (rènrénzǎigē)
- 仰人鼻息
- 仵作行人
- 伏地聖人/伏地圣人
- 伐柯人 (fákērén)
- 仰給於人/仰给于人
- 佣人
- 作人 (zuòrén)
- 佞人
- 伶人 (língrén)
- 何人 (hérén)
- 何人斯
- 伶俐人
- 位極人臣/位极人臣 (wèijírénchén)
- 何許人/何许人 (héxǔrén)
- 侍人
- 來人/来人 (láirén)
- 佼人
- 佳人 (jiārén)
- 來人兒/来人儿
- 佳人命薄
- 佳人才子
- 依人籬下/依人篱下
- 佳人薄命 (jiārénbómìng)
- 信人 (xìnrén)
- 保人 (bǎorén)
- 便人 (biànrén)
- 俚人 (lǐrén)
- 俗人 (súrén)
- 保佐人
- 保見人/保见人
- 保識人/保识人
- 保證人/保证人 (bǎozhèngrén)
- 保護人/保护人
- 保險人/保险人 (bǎoxiǎnrén)
- 個中人/个中人
- 候人
- 倌人
- 個人/个人 (gèrén)
- 倈人/俫人
- 個人主義/个人主义 (gèrén zhǔyì)
- 個人外交/个人外交
- 個人所得/个人所得
- 個人撥接/个人拨接
- 個人本位/个人本位
- 個人秀/个人秀
- 個人衛生/个人卫生 (gèrén wèishēng)
- 個人資料/个人资料
- 個人電腦/个人电脑 (gèrén diànnǎo)
- 個人首頁/个人首页
- 俯仰由人
- 借刀殺人/借刀杀人 (jièdāoshārén)
- 借劍殺人/借剑杀人
- 候選人/候选人 (hòuxuǎnrén)
- 偷人 (tōurén)
- 做人 (zuòrén)
- 偶人 (ǒurén)
- 偉人/伟人 (wěirén)
- 做人家
- 做人情 (zuò rénqíng)
- 做人處事/做人处事
- 假力於人/假力于人
- 偶戲人/偶戏人
- 假手他人 (jiǎshǒutārén)
- 傜人
- 傍人
- 傍人籬壁/傍人篱壁
- 傍人門戶/傍人门户 (bàngrénménhù)
- 傖夫俗人/伧夫俗人
- 傍若無人/傍若无人 (pángruòwúrén)
- 僂人/偻人
- 僇人
- 傷人/伤人 (shāngrén)
- 傭人/佣人
- 傳人/传人 (chuánrén)
- 催人淚下/催人泪下
- 債務人/债务人 (zhàiwùrén)
- 債權人/债权人 (zhàiquánrén)
- 傷殘人/伤残人
- 僱人/雇人
- 僰人
- 僧人 (sēngrén)
- 僕人/仆人 (púrén)
- 僑人/侨人
- 儂人/侬人
- 儷人/俪人
- 元謀猿人/元谋猿人
- 先人 (xiānrén)
- 充人 (chōngrén)
- 先人後己/先人后己
- 光可鑑人/光可鉴人
- 先發制人/先发制人 (xiānfāzhìrén)
- 先聲奪人/先声夺人 (xiānshēngduórén)
- 光身人兒/光身人儿
- 入人
- 內人/内人 (nèirén)
- 內行人/内行人 (nèihángrén)
- 全人 (quánrén)
- 全無人性/全无人性
- 兩性人/两性人 (liǎngxìngrén)
- 兩氏旁人/两氏旁人
- 兩路人/两路人
- 兩重人格/两重人格
- 八九分人
- 八人轎/八人轿
- 八大人覺/八大人觉
- 八大山人
- 公事上人
- 公事人
- 公人 (gōngrén)
- 公務人員/公务人员 (gōngwù rényuán)
- 公家人
- 公教人員/公教人员
- 公斷人/公断人
- 公法人
- 公眾人物/公众人物 (gōngzhòng rénwù)
- 公職人員/公职人员 (gōngzhí rényuán)
- 公訴人/公诉人
- 公證人/公证人 (gōngzhèngrén)
- 共有人
- 典型人物
- 兼人
- 冤人
- 冥王星人 (míngwángxīngrén)
- 冰人 (bīngrén)
- 冰人兒/冰人儿
- 冷眼人
- 冷語侵人/冷语侵人
- 冷語冰人/冷语冰人
- 凌人 (língrén)
- 凡人 (fánrén)
- 凶人
- 出人
- 出人命 (chūrénmìng)
- 出人意外
- 出人意料 (chūrényìliào)
- 出人意表
- 出人頭地/出人头地 (chūréntóudì)
- 出口傷人/出口伤人
- 出家人 (chūjiārén)
- 函人 (hánrén)
- 刀下留人 (dāoxiàliúrén)
- 刑人 (xíngrén)
- 利人
- 別人/别人 (biérén)
- 利人利己
- 利己妨人
- 判若兩人/判若两人 (pànruòliǎngrén)
- 前人 (qiánrén)
- 前無古人/前无古人 (qiánwúgǔrén)
- 前頭人/前头人
- 創辦人/创办人 (chuàngbànrén)
- 力敵萬人/力敌万人
- 功人
- 加人一等
- 功人功狗
- 加害人
- 功狗功人
- 助人 (zhùrén)
- 助人為樂/助人为乐 (zhùrénwéilè)
- 動人/动人 (dòngrén)
- 動人心弦/动人心弦 (dòngrénxīnxián)
- 動人心魄/动人心魄
- 動人肺腑/动人肺腑
- 動人遐思/动人遐思
- 勞人費馬/劳人费马
- 勤雜人員/勤杂人员
- 勾司人
- 勾死人
- 化人場/化人场 (huàrénchǎng)
- 北京人 (Běijīngrén)
- 北京猿人 (Běijīng yuánrén)
- 北人 (běirén)
- 北方人 (běifāngrén)
- 北道主人
- 匠人 (jiàngrén)
- 匪人
- 十全老人
- 千人所指
- 千古罪人 (qiāngǔzuìrén)
- 千差萬差,來人不差/千差万差,来人不差
- 千面人
- 半人半鬼
- 半個人/半个人 (bàn ge rén)
- 卑人
- 南人 (nánrén)
- 卜人
- 占人
- 印人傳/印人传
- 印加人
- 印第安人 (yìndì'ānrén)
- 原人 (yuánrén)
- 原始人 (yuánshǐrén)
- 原班人馬/原班人马
- 友人 (yǒurén)
- 反常人格
- 反面人物 (fǎnmiàn rénwù)
- 受人之託/受人之托
- 受人矚目/受人瞩目
- 取信於人/取信于人
- 受僱人/受雇人
- 受刑人
- 受款人
- 受益人 (shòuyìrén)
- 古人 (gǔrén)
- 可人 (kěrén)
- 古人之風/古人之风
- 古人影子
- 叩人心弦
- 可人意
- 可人憐/可人怜
- 可人憎
- 可意人
- 古道人
- 召集人 (zhàojírén)
- 吉人
- 同人 (tóngrén)
- 名人 (míngrén)
- 各人 (gèrén)
- 吃人 (chīrén)
- 吃人不吐骨頭/吃人不吐骨头
- 吃人兒的/吃人儿的
- 吉人天相 (jíréntiānxiàng)
- 同人女
- 吃人蟲/吃人虫
- 名人達士/名人达士
- 吉卜賽人/吉卜赛人 (jíbǔsàirén)
- 合夥人/合伙人 (héhuǒrén)
- 吃官司人
- 同居人
- 名從主人/名从主人 (míngcóngzhǔrén)
- 吃得苦中苦,方為人上人/吃得苦中苦,方为人上人 (chī de kǔ zhōng kǔ, fāng wéi rén shàng rén)
- 各界人士 (gèjiè rénshì)
- 各白世人
- 同路人 (tónglùrén)
- 告人
- 君人
- 吾人 (wúrén)
- 吹哨人 (chuīshàorén)
- 告密人
- 吹糖人
- 吹糖人兒/吹糖人儿
- 含血噴人/含血喷人 (hánxuèpēnrén)
- 含血噀人
- 吟遊詩人/吟游诗人 (yínyóushīrén)
- 命人
- 咄咄逼人 (duōduōbīrén)
- 哄人
- 咬人狗
- 咬人貓/咬人猫
- 哲人 (zhérén)
- 唐人 (tángrén)
- 哲人其萎
- 唐人街 (tángrénjiē)
- 商人 (shāngrén)
- 唬人
- 喪人/丧人
- 喬人/乔人
- 單人/单人 (dānrén)
- 喊人
- 善人 (shànrén)
- 單人床/单人床 (dānrénchuáng)
- 單人房/单人房 (dānrénfáng)
- 單人旁/单人旁 (dānrénpáng)
- 單人獨馬/单人独马 (dānréndúmǎ)
- 單人車賽/单人车赛
- 喜劇人物/喜剧人物
- 善心人士 (shànxīn rénshì)
- 善氣迎人/善气迎人
- 單立人/单立人 (dānlìrén)
- 善與人交/善与人交
- 善解人意 (shànjiěrényì)
- 善馬熟人/善马熟人
- 嘈人
- 噎人
- 嘴打人
- 噬人菌
- 嚇人/吓人 (xiàrén)
- 嚇人倒怪/吓人倒怪
- 嚇殺人/吓杀人
- 嚇殺人香/吓杀人香 (xiàshārénxiāng)
- 嚼咬人
- 四下無人/四下无人
- 四人幫/四人帮 (sìrénbāng)
- 因人
- 因人成事
- 因人而異/因人而异 (yīnrén'éryì)
- 回頭人/回头人 (huítóurén)
- 困人
- 囿人
- 圉人
- 國人/国人 (guórén)
- 圈外人
- 國際人/国际人
- 國際人格/国际人格
- 國際法人/国际法人
- 土人 (tǔrén)
- 土星人 (tǔxīngrén)
- 土木偶人
- 地下夫人
- 圯上老人
- 地利人和
- 在家人
- 地廣人稀/地广人稀 (dìguǎngrénxī)
- 地廣人稠/地广人稠
- 地方人士 (dìfāng rénshì)
- 地方人情
- 地球人 (dìqiúrén)
- 地瘠人稀
- 地靈人傑/地灵人杰
- 地頭人/地头人
- 坑人
- 報事人/报事人
- 堵人
- 報人/报人 (bàorén)
- 報喜人/报喜人
- 報錄人/报录人
- 壓寨夫人/压寨夫人
- 壞人/坏人 (huàirén)
- 士人 (shìrén)
- 壬人 (rénrén)
- 夏雨雨人 (xiàyǔyùrén)
- 外人 (wàirén)
- 外國人/外国人 (wàiguórén)
- 外場人/外场人
- 外星人 (wàixīngrén)
- 外行人 (wàihángrén)
- 外路人
- 多重人格
- 夜深人靜/夜深人静 (yèshēnrénjìng)
- 夜行人
- 夜闌人靜/夜阑人静 (yèlánrénjìng)
- 大中人
- 大人 (dàrén)
- 大人先生
- 大人國/大人国
- 大人大量
- 大人氣/大人气
- 大人物 (dàrénwù)
- 大人虎變/大人虎变
- 大失人望
- 大孺人
- 大小人兒/大小人儿
- 大忙人 (dàmángrén)
- 大快人心 (dàkuàirénxīn)
- 大恩人
- 大戶人家/大户人家
- 大有人在 (dàyǒurénzài)
- 大紅人/大红人
- 大行人
- 天下人
- 天上人間/天上人间 (tiānshàng rénjiān)
- 天不絕人/天不绝人
- 天人 (tiānrén)
- 夫人 (fūrén)
- 天人之際/天人之际
- 天人交戰/天人交战
- 天人共棄/天人共弃
- 天人合一 (tiānrénhéyī)
- 夫人城
- 天人感應/天人感应
- 天人永隔
- 夫人縣君/夫人县君
- 天人菊
- 夫人裙帶/夫人裙带
- 天人路隔
- 太夫人
- 太子舍人
- 天從人願/天从人愿
- 天心人意 (tiānxīn rényì)
- 天怒人怨 (tiānnùrényuàn)
- 天災人禍/天灾人祸 (tiānzāirénhuò)
- 天無絕人之路/天无绝人之路 (tiān wú jué rén zhī lù)
- 天王星人 (tiānwángxīngrén)
- 天理人情
- 天相吉人
- 太空人 (tàikōngrén)
- 天與人歸/天与人归
- 天賦人權/天赋人权
- 天道人事
- 天隨人願/天随人愿
- 央人
- 央人作伐
- 失業人口/失业人口
- 夸人
- 夷人 (yírén)
- 奇人 (qírén)
- 奄人 (yānrén)
- 奇人異士/奇人异士
- 奪人/夺人
- 女主人 (nǚzhǔrén)
- 女人
- 女人味 (nǚrénwèi)
- 女人國/女人国 (Nǚrénguó)
- 女強人/女强人 (nǚqiángrén)
- 妄人 (wàngrén)
- 奸人 (jiānrén)
- 好人 (hǎorén)
- 好人好事 (hǎorénhǎoshì)
- 好人家 (hǎorénjiā)
- 好人物
- 好人難做/好人难做
- 如夫人
- 好為人師/好为人师 (hàowéirénshī)
- 妙人
- 妖人 (yāorén)
- 妖由人興/妖由人兴
- 妥當人/妥当人
- 妙絕時人/妙绝时人
- 姑丈人
- 姑射神人
- 姦人之雄/奸人之雄
- 婦人/妇人 (fùrén)
- 婦人之仁/妇人之仁 (fùrénzhīrén)
- 婦人家/妇人家 (fùrénjia)
- 婦人生鬚/妇人生须
- 婦人長舌/妇人长舌
- 婢作夫人
- 婢學夫人/婢学夫人
- 婦道人家/妇道人家
- 媒人 (méirén)
- 媒人嘴
- 嫁人 (jiàrén)
- 嫂夫人
- 嫁禍於人/嫁祸于人 (jiàhuòyúrén)
- 嬖人 (bìrén)
- 孤家寡人 (gūjiāguǎrén)
- 學人/学人 (xuérén)
- 學究天人/学究天人
- 學貫天人/学贯天人
- 學際天人/学际天人
- 孺人
- 安人
- 宇宙人 (yǔzhòurén)
- 完人 (wánrén)
- 宜人 (yírén)
- 官人 (guānrén)
- 宗人
- 宗人府
- 官宦人家
- 宦人
- 客人 (kèrén)
- 室人
- 客家人 (Kèjiārén)
- 室邇人遐/室迩人遐
- 室邇人遠/室迩人远
- 家下人
- 家丈人
- 家人 (jiārén)
- 宮人/宫人 (gōngrén)
- 宵人 (xiāorén)
- 害人不淺/害人不浅 (hàirénbùqiǎn)
- 害人利己
- 家人子
- 害人害己 (hàirénhàijǐ)
- 害人精
- 害人蟲/害人虫
- 家大人
- 家敗人亡/家败人亡
- 害死人
- 家破人亡 (jiāpòrénwáng)
- 家給人足/家给人足
- 家至人說/家至人说
- 寄人籬下/寄人篱下 (jìrénlíxià)
- 寂若無人/寂若无人
- 富人 (fùrén)
- 寒人
- 寓人寓馬/寓人寓马
- 寒氣襲人/寒气袭人
- 寒氣逼人/寒气逼人
- 富貴人家/富贵人家
- 富貴逼人/富贵逼人
- 富貴驕人/富贵骄人
- 寡人 (guǎrén)
- 審己度人/审己度人
- 寸馬豆人/寸马豆人
- 寺人 (sìrén)
- 封人 (fēngrén)
- 封面人物 (fēngmiàn rénwù)
- 專人/专人 (zhuānrén)
- 專業人員/专业人员 (zhuānyè rényuán)
- 專業人才/专业人才 (zhuānyè réncái)
- 尊人
- 尊夫人 (zūnfūrén)
- 尊己卑人
- 小主人
- 小人 (xiǎorén)
- 小人兒/小人儿
- 小人兒書/小人儿书
- 小人國/小人国
- 小人家
- 小人得志 (xiǎoréndézhì)
- 小人樣/小人样
- 小人殉財/小人殉财
- 小人物 (xiǎorénwù)
- 小夫人
- 小女人
- 小婦人/小妇人
- 小官人
- 小戶人家/小户人家
- 小灰人 (xiǎohuīrén)
- 小紅人/小红人 (xiǎohóngrén)
- 小綠人/小绿人 (xiǎolǜrén)
- 小舍人
- 小藍人/小蓝人 (xiǎolánrén)
- 小頂人/小顶人
- 小鳥依人/小鸟依人 (xiǎoniǎoyīrén)
- 小黃人/小黄人 (xiǎohuángrén)
- 少年人
- 尤人
- 就裡人/就里人
- 局內人/局内人 (júnèirén)
- 局外人 (júwàirén)
- 屁鳥人/屁鸟人
- 居人 (jūrén)
- 居停主人
- 屈己待人 (qūjǐ dàirén)
- 屈己從人/屈己从人
- 屋裡人/屋里人 (wūlǐrén)
- 屬人法/属人法
- 山人 (shānrén)
- 山頂洞人/山顶洞人
- 崇明人拉阿爹
- 工人 (gōngrén)
- 工人運動/工人运动
- 巨人 (jùrén)
- 巨人族
- 巨人症 (jùrénzhèng)
- 左鎮人/左镇人
- 差人
- 差強人意/差强人意
- 巴人 (bārén)
- 巴人下里
- 巴人調/巴人调
- 巴斯克人
- 市井之人
- 市井小人
- 市人
- 希伯來人/希伯来人 (xībóláirén)
- 師人/师人
- 常人 (chángrén)
- 帶球撞人/带球撞人
- 干證人
- 平人 (píngrén)
- 平常人 (píngchángrén)
- 平常人家
- 平易近人 (píngyìjìnrén)
- 并介之人
- 幹人/干人
- 幻人
- 幽人
- 幽靈人口/幽灵人口
- 床頭人/床头人
- 底下人 (dǐxiarén)
- 庖人 (páorén)
- 底腳裡人/底脚里人
- 庶人 (shùrén)
- 庸人 (yōngrén)
- 庸人自擾/庸人自扰 (yōngrénzìrǎo)
- 廋人
- 廄人/厩人
- 廓爾喀人/廓尔喀人
- 廚人/厨人 (chúrén)
- 廢人/废人 (fèirén)
- 廣告人/广告人
- 弋人何篡
- 弓人 (gōngrén)
- 引人 (yǐnrén)
- 引人側目/引人侧目
- 引人入勝/引人入胜 (yǐnrénrùshèng)
- 引人注目 (yǐnrénzhùmù)
- 引人矚目/引人瞩目
- 引人遐思
- 引人非議/引人非议
- 引水人 (yínshuǐrén)
- 引路人
- 強人/强人 (qiángrén)
- 強人所難/强人所难 (qiǎngrénsuǒnán)
- 影人
- 影戲人兒/影戏人儿
- 征人
- 待人 (dàirén)
- 後人/后人 (hòurén)
- 待人接物 (dàirénjiēwù)
- 待人處世/待人处世
- 待人處事/待人处事
- 後備軍人/后备军人
- 後發制人/后发制人 (hòufāzhìrén)
- 後繼乏人/后继乏人
- 後繼有人/后继有人
- 後繼無人/后继无人 (hòujìwúrén)
- 徒亂人意/徒乱人意
- 從井救人/从井救人
- 御人
- 從人/从人 (cóngrén)
- 得人
- 得人兒/得人儿
- 得人心 (dérénxīn)
- 得人意
- 得人死力
- 得失在人
- 從業人員/从业人员 (cóngyè rényuán)
- 循循誘人/循循诱人
- 心上人 (xīnshàngrén)
- 志士仁人 (zhìshìrénrén)
- 快人 (kuàirén)
- 快人快語/快人快语
- 怪人 (guàirén)
- 怕人 (pàrén)
- 急人之困
- 急人之難/急人之难
- 怕人子
- 怕人設設/怕人设设
- 怨天尤人 (yuàntiān-yóurén)
- 性情中人 (xìngqíngzhōngrén)
- 息事寧人/息事宁人 (xīshìníngrén)
- 恨人
- 恭人 (gōngrén)
- 恩人 (ēnrén)
- 恃勢凌人
- 息夫人
- 恥居人下/耻居人下
- 恕己及人
- 恭己待人
- 悅人/悦人
- 惡人/恶人 (èrén)
- 悶人/闷人
- 情人 (qíngrén)
- 惡人先告狀/恶人先告状 (èrén xiān gàozhuàng)
- 情人果
- 情人節/情人节 (Qíngrénjié)
- 惡人自有惡人磨/恶人自有恶人磨
- 悲天憫人/悲天悯人 (bēitiānmǐnrén)
- 惡語傷人/恶语伤人
- 惡語傷人六月寒/恶语伤人六月寒
- 意中人 (yìzhōngrén)
- 惱人/恼人 (nǎorén)
- 愛人/爱人 (àirén)
- 感人 (gǎnrén)
- 愚人 (yúrén)
- 愛人以德/爱人以德
- 愛人兒/爱人儿
- 愛人好士/爱人好士
- 愛人如己/爱人如己 (àirénrújǐ)
- 感人心曲
- 感人心脾
- 惹人憐愛/惹人怜爱 (rěrénlián'ài)
- 愚人節/愚人节 (Yúrénjié)
- 感人肺肝 (gǎnrénfèigān)
- 感人肺腑 (gǎnrénfèifǔ)
- 惺惺人 (xīngxīngrén)
- 惺惺道人
- 慈悲殺人/慈悲杀人 (cíbēi shārén)
- 愧汗怍人
- 憂愁夫人/忧愁夫人
- 慘無人道/惨无人道 (cǎnwúréndào)
- 慘絕人寰/惨绝人寰 (cǎnjuérénhuán)
- 憂能傷人/忧能伤人
- 應乎人心/应乎人心
- 憸人/𪫺人
- 應天從人/应天从人
- 應天順人/应天顺人 (yìngtiānshùnrén)
- 懶人/懒人 (lǎnrén)
- 懶人植物/懒人植物
- 懾人/慑人
- 懾人心魄/慑人心魄
- 戀人/恋人 (liànrén)
- 成事在人
- 成人 (chéngrén)
- 成人之美 (chéngrénzhīměi)
- 成人教育 (chéngrén jiàoyù)
- 成人病
- 成人電影/成人电影 (chéngrén diànyǐng)
- 成敗論人/成败论人
- 或人
- 戰鬥人員/战斗人员
- 戶告人曉/户告人晓
- 戶給人足/户给人足
- 所嫁非人
- 所有人 (suǒyǒurén)
- 所託非人/所托非人 (suǒtuōfēirén)
- 手下人
- 才人 (cáirén)
- 才子佳人 (cáizǐ jiārén)
- 才秀人微
- 打人 (dǎrén)
- 打人罵狗/打人骂狗
- 扣人心弦 (kòurénxīnxián)
- 托缽人/托钵人
- 抗戰夫人/抗战夫人
- 技術人員/技术人员 (jìshù rényuán)
- 投資人/投资人 (tóuzīrén)
- 把門人/把门人
- 招人
- 招人物議/招人物议
- 拖人落水
- 押寨夫人
- 拐帶人口/拐带人口
- 拋閃殺人/抛闪杀人
- 拿人
- 拾人涕唾
- 拾人牙慧 (shírényáhuì)
- 持人長短/持人长短
- 拱手讓人/拱手让人 (gǒngshǒuràngrén)
- 拾糞人/拾粪人
- 指路人
- 捉事人
- 捕人
- 挨人兒/挨人儿
- 挾人捉將/挟人捉将
- 捉刀人
- 振奮人心/振奋人心 (zhènfènrénxīn)
- 捉將挾人/捉将挟人
- 捏麵人/捏面人
- 探事人
- 掠人之美
- 授人以柄 (shòu rén yǐ bǐng)
- 授人口實/授人口实
- 掩人耳目 (yǎnrén'ěrmù)
- 捨命救人/舍命救人
- 掘墓人 (juémùrén)
- 推己及人 (tuījǐjírén)
- 捨己就人/舍己就人
- 捨己從人/舍己从人
- 捨己成人/舍己成人
- 捨己救人/舍己救人
- 捨己為人/舍己为人 (shějǐwèirén)
- 接棒人 (jiēbàngrén)
- 接班人 (jiēbānrén)
- 探細人/探细人
- 採芹人/采芹人
- 推賢任人/推贤任人
- 探軍人/探军人
- 掌門人/掌门人 (zhǎngménrén)
- 揢人
- 提人
- 揍人
- 提示人
- 損人/损人
- 損人不利己/损人不利己 (sǔnrén bù lìjǐ)
- 損人利己/损人利己 (sǔnrénlìjǐ)
- 損人安己/损人安己
- 損人益己/损人益己
- 損人肥己/损人肥己
- 摩爾人/摩尔人 (mó'ěrrén)
- 摩耶夫人
- 撧人/𪮖人
- 撣人/掸人
- 撩人
- 撲人鼻子/扑人鼻子
- 撒手人寰 (sāshǒurénhuán)
- 撰稿人
- 撅豎小人/撅竖小人
- 撾人/挝人
- 撼人
- 擄人勒贖/掳人勒赎
- 擔人情/担人情
- 擋人牌/挡人牌
- 擇人而事/择人而事
- 擬人/拟人 (nǐrén)
- 擬人化/拟人化 (nǐrénhuà)
- 擬人法/拟人法
- 擾人/扰人
- 擾人清夢/扰人清梦 (rǎorénqīngmèng)
- 攘人之美
- 攤了人命/摊了人命
- 收件人 (shōujiànrén)
- 收攬人心/收揽人心 (shōulǎnrénxīn)
- 放人
- 放人一馬/放人一马
- 政通人和 (zhèngtōngrénhé)
- 故人 (gùrén)
- 救人 (jiùrén)
- 敝人 (bìrén)
- 散人
- 敬授人時/敬授人时
- 敵人/敌人 (dírén)
- 整人 (zhěngrén)
- 整人遊戲/整人游戏
- 文人 (wénrén)
- 文人畫/文人画
- 文人相輕/文人相轻 (wénrénxiāngqīng)
- 文人雅士
- 文化人 (wénhuàrén)
- 文如其人 (wénrúqírén)
- 文明人 (wénmíngrén)
- 斐濟人/斐济人
- 斗南一人
- 斗筲之人
- 斯文人
- 新人 (xīnrén)
- 新人物
- 新人類/新人类 (xīnrénlèi)
- 新好女人
- 新好男人
- 新新人類/新新人类 (xīnxīnrénlèi)
- 新聞人物/新闻人物
- 新鮮人/新鲜人 (xīnxiānrén)
- 方人
- 方外之人
- 方外人
- 旅人 (lǚrén)
- 旁人 (pángrén)
- 旁人短長/旁人短长
- 旅人蕉
- 旁若無人/旁若无人 (pángruòwúrén)
- 旁邊人/旁边人
- 族人 (zúrén)
- 旗人 (qírén)
- 明人 (míngrén)
- 易人 (yìrén)
- 昔人 (xīrén)
- 明人不說暗話/明人不说暗话
- 明格列爾人/明格列尔人 (mínggéliè'ěrrén)
- 明白人 (míngbairén)
- 明眼人 (míngyǎnrén)
- 明豔動人/明艳动人
- 春歸人老/春归人老
- 春色惱人/春色恼人
- 是非人我
- 春風風人/春风风人 (chūnfēngfèngrén)
- 時人/时人 (shírén)
- 智人 (zhìrén)
- 普通人 (pǔtōngrén)
- 暍人
- 暗箭中人
- 暗箭傷人/暗箭伤人 (ànjiànshāngrén)
- 曉人/晓人
- 曠代一人/旷代一人
- 曠古一人/旷古一人
- 曲盡人情/曲尽人情
- 曲終人散/曲终人散 (qǔzhōngrénsàn)
- 更深人靜/更深人静
- 更生人
- 更闌人靜/更阑人静
- 替人
- 曾參殺人/曾参杀人 (Zēng Shēn shārén)
- 月下老人 (Yuèxià Lǎorén)
- 月亮人
- 有了人家
- 有人 (yǒurén)
- 有人家
- 有人緣兒/有人缘儿
- 有心人 (yǒuxīnrén)
- 有我無人/有我无人
- 有色人種/有色人种 (yǒusè rénzhǒng)
- 有錢人/有钱人 (yǒuqiánrén)
- 朝暮人
- 木人石心
- 木偶人
- 木星人 (mùxīngrén)
- 木頭人/木头人 (mùtourén)
- 未亡人 (wèiwángrén)
- 本人 (běnrén)
- 本地人 (běndìrén)
- 未成年人 (wèichéngniánrén)
- 末路人
- 杠人
- 材人
- 村人 (cūnrén)
- 杞人之憂/杞人之忧
- 杞人憂天/杞人忧天 (qǐrényōutiān)
- 東人/东人 (dōngrén)
- 枉己正人
- 東方人/东方人 (dōngfāngrén)
- 東洋人/东洋人 (dōngyángrén)
- 杳無人煙/杳无人烟 (yǎowúrényān)
- 杳無人跡/杳无人迹
- 枉道事人
- 枕邊人/枕边人 (zhěnbiānrén)
- 東野巴人/东野巴人
- 染人
- 某人 (mǒurén)
- 柯人
- 柏柏人
- 校人
- 栽人
- 桐人
- 桃人
- 桂冠詩人/桂冠诗人
- 桃花人面
- 梓人
- 梢人
- 棘人
- 植物人 (zhíwùrén)
- 業人/业人
- 楖人
- 榜人
- 榮譽軍人/荣誉军人 (róngyù jūnrén)
- 樂人/乐人
- 樹人/树人 (shùrén)
- 機伶人/机伶人
- 機器人/机器人 (jīqìrén)
- 欲人不知,莫若勿為/欲人不知,莫若勿为
- 欺人之談/欺人之谈
- 欺人太甚 (qīréntàishèn)
- 欺人自欺
- 欺天罔人
- 款款動人/款款动人
- 正人 (zhèngrén)
- 正人君子 (zhèngrénjūnzǐ)
- 正面人物
- 步人後塵/步人后尘 (bùrénhòuchén)
- 武人 (wǔrén)
- 歪嘴喊人
- 歸人/归人 (guīrén)
- 歸國學人/归国学人
- 歹人 (dǎirén)
- 死人 (sǐrén)
- 殃人貨/殃人货
- 殢人/𣨼人 (tìrén)
- 殺人償命/杀人偿命
- 殺人如芥/杀人如芥
- 殺人如草/杀人如草
- 殺人如蓺/杀人如蓺
- 殺人如麻/杀人如麻 (shārénrúmá)
- 殺人放火/杀人放火 (shārénfànghuǒ)
- 殺人滅口/杀人灭口 (shārénmièkǒu)
- 殺人滅跡/杀人灭迹
- 殺人犯/杀人犯 (shārénfàn)
- 殺人盈野/杀人盈野
- 殺人罪/杀人罪
- 殺人越貨/杀人越货 (shārényuèhuò)
- 母語人士/母语人士 (mǔyǔ rénshì)
- 每人 (měirén)
- 比肩人
- 毛人
- 毛利人 (Máolìrén)
- 毛子人
- 民人 (mínrén)
- 水上人家
- 水星人 (shuǐxīngrén)
- 求人 (qiúrén)
- 江湖藝人/江湖艺人
- 江米人
- 沒事人/没事人 (méishìrén)
- 沒人/没人
- 沖人/冲人
- 沒人味/没人味
- 沒人形/没人形
- 沁人心肺
- 沁人心脾 (qìnrénxīnpí)
- 沒人煙/没人烟
- 沁人肺腑
- 沒人處/没人处
- 沒有人/没有人
- 沖虛真人/冲虚真人
- 泥人 (nírén)
- 法人 (fǎrén)
- 治人
- 泥人張/泥人张
- 法利賽人/法利赛人 (Fǎlìsàirén)
- 法定人數/法定人数 (fǎdìng rénshù)
- 泥足巨人
- 活不見人死不見屍/活不见人死不见尸 (huó bù jiàn rén sǐ bù jiàn shī)
- 洋人 (yángrén)
- 流人 (liúrén)
- 活人妻
- 流動人口/流动人口 (liúdòng rénkǒu)
- 活埋人
- 活死人
- 派用人員/派用人员
- 活要見人,死要見屍/活要见人,死要见尸 (huó yào jiàn rén, sǐ yào jiàn shī)
- 浪人 (làngrén)
- 涓人
- 浼人親行/浼人亲行
- 海夫人
- 浮浪人
- 海王星人 (hǎiwángxīngrén)
- 淑人
- 深人
- 清人 (qīngrén)
- 混人
- 淚人兒/泪人儿 (lèirénr)
- 淑人君子
- 深入人心 (shēnrùrénxīn)
- 淪落人/沦落人
- 淨身人/净身人
- 渾人/浑人
- 湘夫人
- 游戲人間/游戏人间
- 游手人戶/游手人户
- 湖畔詩人/湖畔诗人
- 滅絕人性/灭绝人性
- 漁人/渔人 (yúrén)
- 滿人/满人 (mǎnrén)
- 漢人/汉人 (Hànrén)
- 漁人之利/渔人之利 (yúrénzhīlì)
- 漁人得利/渔人得利 (yúréndélì)
- 演藝人員/演艺人员
- 漸通人事/渐通人事
- 潔己愛人/洁己爱人
- 潑賤人/泼贱人
- 潑墨人物/泼墨人物
- 澤人/泽人
- 濟世安人/济世安人
- 濟世救人/济世救人
- 濟人/济人
- 濟人利物/济人利物
- 濫好人/滥好人 (lànhǎorén)
- 火工道人
- 火星人 (huǒxīngrén)
- 炎陽炙人/炎阳炙人
- 為人/为人
- 為人作嫁/为人作嫁
- 為人師表/为人师表 (wéirénshībiǎo)
- 為人為徹/为人为彻
- 為人行事/为人行事
- 為人解圍/为人解围
- 無人之地/无人之地
- 無人之境/无人之境 (wúrénzhījìng)
- 無人作主/无人作主
- 無人問津/无人问津 (wúrénwènjīn)
- 無人銀行/无人银行
- 無人飛機/无人飞机 (wúrén fēijī)
- 煩人/烦人 (fánrén)
- 煙霞外人/烟霞外人
- 熏人
- 熟人 (shúrén)
- 熟面人
- 燕市酒人
- 燧人氏
- 爛好人/烂好人 (lànhǎorén)
- 爪哇人 (Zhǎowārén)
- 牆倒眾人推/墙倒众人推 (qiáng dǎo zhòngrén tuī)
- 牙人 (yárén)
- 牛人 (niúrén)
- 牧人 (mùrén)
- 物是人非 (wùshìrénfēi)
- 犯人 (fànrén)
- 狂人 (kuángrén)
- 狗仗人勢/狗仗人势
- 狗眼烏珠看人低/狗眼乌珠看人低
- 狗眼看人低 (gǒuyǎn kàn rén dī)
- 狼人 (lángrén)
- 猶太人/犹太人 (yóutàirén)
- 獃人/呆人
- 猿人 (yuánrén)
- 獄人/狱人
- 獵人/猎人 (lièrén)
- 獶人
- 獸人/兽人 (shòurén)
- 獸化人/兽化人 (shòuhuàrén)
- 獸心人面/兽心人面
- 獿人
- 率獸食人/率兽食人
- 王人
- 王公大人
- 王公貴人/王公贵人
- 玉人 (yùrén)
- 玩人喪德/玩人丧德
- 理人 (lǐrén)
- 現代人/现代人 (xiàndàirén)
- 現役軍人/现役军人
- 璧人 (bìrén)
- 甘草人物
- 甚人
- 生人 (shēngrén)
- 生意人 (shēngyirén)
- 產業工人/产业工人 (chǎnyè gōngrén)
- 用人 (yòngrén)
- 用非其人
- 由人
- 田園詩人/田园诗人
- 男人
- 男人婆 (nánrénpó)
- 留美學人/留美学人
- 異人/异人 (yìrén)
- 異士奇人/异士奇人
- 異鄉人/异乡人
- 異類之人/异类之人
- 異香襲人/异香袭人
- 畫中人/画中人
- 當事人/当事人 (dāngshìrén)
- 畸人
- 當家人/当家人
- 當頭人/当头人
- 疑人疑鬼
- 疑人竊鈇/疑人窃𫓧
- 病人 (bìngrén)
- 痴人 (chīrén)
- 痴人痴福
- 痴人說夢/痴人说梦 (chīrénshuōmèng)
- 瘋人院/疯人院 (fēngrényuàn)
- 瘖啞人/瘖哑人
- 瘠人肥己
- 瘠己肥人
- 發人深省/发人深省 (fārénshēnxǐng)
- 發行人/发行人 (fāxíngrén)
- 發言人/发言人 (fāyánrén)
- 發起人/发起人 (fāqǐrén)
- 白人 (báirén)
- 白人情
- 白嚼人
- 白屋人家
- 白席人
- 白相人
- 白石道人
- 白種人/白种人 (báizhǒngrén)
- 白色人種/白色人种 (báisè rénzhǒng)
- 白衣人 (báiyīrén)
- 白身人 (báishēnrén)
- 白頭人送黑頭人/白头人送黑头人 (báitóu rén sòng hēitóu rén)
- 白髮人送黑髮人/白发人送黑发人 (báifàrén sòng hēifàrén)
- 百世之人
- 百年樹人/百年树人 (bǎiniánshùrén)
- 皁衣人/皂衣人
- 皇天不負苦心人/皇天不负苦心人 (huángtiān bù fù kǔxīn rén)
- 盛氣凌人 (shèngqìlíngrén)
- 盛氣臨人/盛气临人
- 盜怨主人/盗怨主人
- 盜憎主人/盗憎主人
- 盡人/尽人
- 盡人事/尽人事 (jìnrénshì)
- 盡人情/尽人情
- 盡人皆知/尽人皆知 (jìnrénjiēzhī)
- 盡如人意/尽如人意 (jìnrúrényì)
- 監察人/监察人
- 監護人/监护人 (jiānhùrén)
- 目中無人/目中无人 (mùzhōngwúrén)
- 目擊證人/目击证人 (mùjī zhèngrén)
- 目若無人/目若无人
- 盯人
- 盯人防守
- 盲人 (mángrén)
- 盲人把燭/盲人把烛
- 盲人摸象 (mángrénmōxiàng)
- 盲人瞎馬/盲人瞎马 (mángrénxiāmǎ)
- 盲人說象/盲人说象
- 盲人讀物/盲人读物
- 盲人電腦/盲人电脑
- 直立人 (zhílìrén)
- 直道事人
- 相人
- 相人偶
- 看人挑擔不吃力/看人挑担不吃力
- 看人挑擔勿吃力/看人挑担勿吃力
- 看人眉睫
- 看人行事
- 眩人 (xuànrén)
- 真人 (zhēnrén)
- 真人不露相 (zhēnrén bù lòuxiàng)
- 真人真事 (zhēnrénzhēnshì)
- 真人秀 (zhēnrénxiù)
- 眼中人
- 眾人/众人 (zhòngrén)
- 睹物思人 (dǔwùsīrén)
- 睹物懷人/睹物怀人
- 睡美人 (Shuìměirén)
- 瞞人/瞒人
- 瞞人眼目/瞒人眼目
- 瞳人 (tóngrén)
- 矜人 (jīnrén)
- 矢人 (shǐrén)
- 知人 (zhīrén)
- 知人下士
- 知人之明 (zhīrénzhīmíng)
- 知人善任 (zhīrénshànrèn)
- 知人料事
- 知人知面不知心 (zhī rén zhī miàn bù zhī xīn)
- 知人知面勿知心
- 知人論世/知人论世
- 矮人 (ǎirén)
- 矮人一截
- 矮人族
- 矮人看場/矮人看场
- 矮人觀場/矮人观场 (ǎirénguānchǎng)
- 石人
- 碩人/硕人 (shuòrén)
- 磨人 (mórén)
- 神人 (shénrén)
- 神人共悅/神人共悦
- 神人共戮
- 神人鑒知/神人鉴知
- 神仙中人 (shénxiānzhōngrén)
- 祗候人
- 祕密證人/秘密证人
- 神怒人怨
- 神怒人棄/神怒人弃
- 神職人員/神职人员 (shénzhí rényuán)
- 視人如傷/视人如伤
- 視人如子/视人如子
- 視人畏傷/视人畏伤
- 福人
- 禍福惟人/祸福惟人
- 禍福由人/祸福由人
- 禮教吃人/礼教吃人
- 禮順人情/礼顺人情
- 萬人/万人 (wànrén)
- 萬人之敵/万人之敌
- 萬人坑/万人坑 (wànrénkēng)
- 萬人敵/万人敌
- 萬人空巷/万人空巷 (wànrénkōngxiàng)
- 萬人迷/万人迷 (wànrénmí)
- 私人 (sīrén)
- 秀才人情
- 秋水伊人
- 秋草人情
- 稅務人員/税务人员
- 稠人 (chóurén)
- 稠人廣坐/稠人广坐 (chóurén guǎngzuò)
- 稠人廣眾/稠人广众
- 種人/种人
- 稿人
- 稻草人 (dàocǎorén)
- 穎悟絕人/颖悟绝人
- 空中飛人/空中飞人 (kōngzhōngfēirén)
- 空身人兒/空身人儿
- 窩停主人/窝停主人
- 窮人/穷人 (qióngrén)
- 窶人子/窭人子
- 立人
- 立人兒/立人儿
- 立人達人/立人达人
- 端人
- 端人正士
- 竹夫人 (zhúfūrén)
- 第一人
- 第一人稱/第一人称 (dì-yī rénchēng)
- 第一夫人 (dì-yī fūrén)
- 第三人稱/第三人称 (dì-sān rénchēng)
- 等人 (děngrén)
- 等閒人物/等闲人物
- 節人/节人
- 節用愛人/节用爱人
- 管夫人
- 篙人
- 粗人 (cūrén)
- 精力過人/精力过人
- 精彩逼人
- 糖人兒/糖人儿
- 糙人
- 紅人/红人 (hóngrén)
- 紅種人/红种人 (hóngzhǒngrén)
- 紅粉佳人/红粉佳人 (hóngfěnjiārén)
- 紅頂商人/红顶商人 (hóngdǐng shāngrén)
- 紙人/纸人 (zhǐrén)
- 素人畫家/素人画家
- 素口罵人/素口骂人
- 累人 (lèirén)
- 細人/细人
- 細探人/细探人
- 絕世佳人/绝世佳人
- 絕人/绝人
- 絕代佳人/绝代佳人
- 絳幘雞人/绛帻鸡人
- 絕色佳人/绝色佳人 (juésèjiārén)
- 結髮人/结发人
- 經濟人/经济人
- 經濟人權/经济人权
- 經紀人/经纪人 (jīngjìrén)
- 經紀人家/经纪人家
- 維京人/维京人 (wéijīngrén)
- 綠人/绿人
- 維吾爾人/维吾尔人 (wéiwú'ěrrén)
- 緊迫盯人/紧迫盯人
- 線人/线人 (xiànrén)
- 編人/编人
- 編輯人/编辑人
- 縛稿為人/缚稿为人
- 織女星人/织女星人 (zhīnǚxīngrén)
- 繼承人/继承人 (jìchéngrén)
- 纖人/纤人 (xiānrén)
- 罪人 (zuìrén)
- 罪人不孥
- 罪人不帑
- 罵人/骂人 (màrén)
- 羅真人/罗真人
- 美人 (měirén)
- 美人兒/美人儿 (měirénr)
- 美人命薄
- 美人尖 (měirénjiān)
- 美人局
- 美人拳
- 美人樹/美人树
- 美人燈兒/美人灯儿 (měiréndēngr)
- 美人癆/美人痨 (měirénláo)
- 美人胚子
- 美人胎子
- 美人蕉 (měirénjiāo)
- 美人計/美人计 (měirénjì)
- 美人遲暮/美人迟暮
- 美人香草
- 美人魚/美人鱼 (měirényú)
- 美澤鑑人/美泽鉴人
- 羞人 (xiūrén)
- 羞人答答
- 羞面見人/羞面见人
- 義人/义人 (yìrén)
- 羲皇上人
- 羽人 (yǔrén)
- 翳桑餓人/翳桑饿人
- 老丈人
- 老人 (lǎorén)
- 老人問題/老人问题
- 老人學/老人学 (lǎorénxué)
- 老人家
- 老人年金
- 老人星 (Lǎorénxīng)
- 老人會/老人会
- 老人福利
- 老人節/老人节
- 老人與海/老人与海
- 老人茶
- 老人院 (lǎorényuàn)
- 老作人
- 老好人 (lǎohǎorén)
- 老婦人/老妇人 (lǎofùrén)
- 老實人/老实人
- 老年人 (lǎoniánrén)
- 老年人口
- 老成人
- 耐人尋味/耐人寻味 (nàirénxúnwèi)
- 耶誕老人/耶诞老人 (Yēdàn Lǎorén)
- 聖人/圣人 (shèngrén)
- 聖人諱/圣人讳 (shèngrénhuì)
- 聘用人員/聘用人员
- 聖誕老人/圣诞老人 (Shèngdàn Lǎorén)
- 聞人/闻人
- 聳人聽聞/耸人听闻 (sǒngréntīngwén)
- 聰明人/聪明人 (cōngmíngrén)
- 聾人/聋人 (lóngrén)
- 聽人/听人 (tīngrén)
- 聽人穿鼻/听人穿鼻
- 肉人
- 肝膽照人/肝胆照人
- 背人 (bèirén)
- 胡人 (Húrén)
- 能人 (néngrén)
- 腐人
- 腓尼基人
- 腳下人/脚下人
- 腳底下人/脚底下人
- 膾炙人口/脍炙人口 (kuàizhìrénkǒu)
- 臥人兒/卧人儿
- 臧否人物
- 臨水夫人/临水夫人
- 自助人助
- 自娛娛人/自娱娱人
- 自家人 (zìjiārén)
- 自己人 (zìjǐrén)
- 自欺欺人 (zìqīqīrén)
- 自然人 (zìránrén)
- 自訴人/自诉人
- 至人 (zhìrén)
- 至人無夢/至人无梦
- 與人為善/与人为善 (yǔrénwéishàn)
- 舉人/举人 (jǔrén)
- 舊人/旧人
- 舌人 (shérén)
- 舍人 (shèrén)
- 舍己從人/舍己从人
- 舍己芸人
- 舟人
- 良人 (liángrén)
- 色目人 (Sèmùrén)
- 艾人
- 花蕊夫人
- 苗人 (miáorén)
- 苦人
- 英氣逼人/英气逼人
- 若而人
- 若要人不知,除非己莫為/若要人不知,除非己莫为 (ruò yào rén bùzhī chúfēi jǐ mò wéi)
- 草人 (cǎorén)
- 荒無人煙/荒无人烟
- 草菅人命 (cǎojiānrénmìng)
- 莊稼人/庄稼人
- 華人/华人 (Huárén)
- 菲人事
- 著人/着人
- 落人口實/落人口实
- 落人笑柄
- 落花媒人
- 蓋人/盖人
- 蒙古人種/蒙古人种 (měnggǔ rénzhǒng)
- 蓑衣丈人
- 蓬蒿人
- 薄倖人/薄幸人
- 藍田猿人/蓝田猿人
- 藝人/艺人 (yìrén)
- 蘇美人/苏美人
- 虎人 (hǔrén)
- 處世待人/处世待人
- 虛己受人/虚己受人
- 虞人
- 虞美人 (yúměirén)
- 蛇蠍美人/蛇蝎美人 (shéxiē měirén)
- 蛙人 (wārén)
- 蛙人操
- 蝙蝠人
- 蝴蝶夫人
- 蠟人/蜡人
- 蠢人 (chǔnrén)
- 蠟人館/蜡人馆
- 蠱惑人心/蛊惑人心
- 蠻人/蛮人 (mánrén)
- 血口噴人/血口喷人 (xuèkǒupēnrén)
- 行人 (xíngrén)
- 行人情
- 衙院人家
- 衣冠中人
- 被保險人/被保险人 (bèibǎoxiǎnrén)
- 被害人 (bèihàirén)
- 被繼承人/被继承人 (bèijìchéngrén)
- 被論人/被论人
- 被選舉人/被选举人
- 製作人/制作人 (zhìzuòrén)
- 襲人/袭人
- 襲人故智/袭人故智
- 西人 (xīrén)
- 西洋人 (xīyángrén)
- 西臺人/西台人
- 要人 (yàorén)
- 要人好看
- 要約人/要约人
- 見不得人/见不得人
- 見人/见人
- 見笑於人/见笑于人
- 見證人/见证人 (jiànzhèngrén)
- 親人/亲人 (qīnrén)
- 觀護人/观护人
- 解人
- 言人人殊 (yánrénrénshū)
- 訓人/训人
- 討人/讨人 (tǎorén)
- 託人情/托人情
- 討人情/讨人情
- 討海人/讨海人 (tǎohǎirén)
- 訛人/讹人 (érén)
- 訪山人/访山人
- 詞人/词人
- 評判人/评判人
- 詩人/诗人 (shīrén)
- 詩人節/诗人节
- 詩禮人家/诗礼人家
- 語不擇人/语不择人
- 語不驚人/语不惊人
- 誤人/误人
- 誘人/诱人 (yòurén)
- 誒人/诶人 (ê̄rén)
- 誨人不倦/诲人不倦 (huìrénbùjuàn)
- 誤人子弟/误人子弟 (wùrénzǐdì)
- 說人情/说人情
- 說書人/说书人 (shuōshūrén)
- 說話人/说话人
- 認養人/认养人
- 諕人/𬤀人
- 調人/调人
- 誰人/谁人
- 調停人/调停人
- 謀事在人/谋事在人
- 謀人/谋人
- 謀及婦人/谋及妇人
- 諜報人員/谍报人员
- 諾曼人/诺曼人 (nuòmànrén)
- 譖人/谮人
- 證人/证人 (zhèngrén)
- 證婚人/证婚人
- 讀書人/读书人 (dúshūrén)
- 變性人/变性人 (biànxìngrén)
- 讒人/谗人
- 豎人毛髮/竖人毛发
- 象人 (xiàngrén)
- 貌不驚人/貌不惊人
- 貓人/猫人 (māorén)
- 貞人/贞人 (zhēnrén)
- 負心人/负心人 (fùxīnrén)
- 負責人/负责人 (fùzérén)
- 財團法人/财团法人
- 販賣人口/贩卖人口
- 貧賤驕人/贫贱骄人
- 貴人/贵人 (guìrén)
- 買人事/买人事
- 貽人口實/贻人口实
- 貴人多忘/贵人多忘
- 貼心人/贴心人
- 貴極人臣/贵极人臣
- 買賣人/买卖人 (mǎimàirén)
- 買賣人口/买卖人口
- 賊人/贼人 (zéirén)
- 賈人/贾人 (gǔrén)
- 賊人心虛/贼人心虚
- 賈人渡河/贾人渡河
- 賊人膽虛/贼人胆虚
- 賢人/贤人 (xiánrén)
- 賤人/贱人 (jiànrén)
- 賨人/𰷥人
- 賣人情/卖人情
- 賣野人頭/卖野人头
- 贊助人/赞助人
- 起訴人/起诉人 (qǐsùrén)
- 超人 (chāorén)
- 趁人不備/趁人不备
- 趁人之危
- 越人視秦/越人视秦
- 超人論/超人论
- 趕趁人/赶趁人
- 足了十人
- 跑封人
- 跟了人
- 路人 (lùrén)
- 跟前人
- 路岐人
- 路斷人稀/路断人稀
- 路絕人稀/路绝人稀
- 躁人辭多/躁人辞多
- 身邊人/身边人 (shēnbiānrén)
- 車人/车人
- 車毀人亡/车毁人亡 (chēhuǐrénwáng)
- 車馬人兒/车马人儿
- 軍人/军人 (jūnrén)
- 軍人節/军人节
- 軍人魂/军人魂
- 軟人才/软人才
- 輔佐人/辅佐人
- 輪人/轮人
- 輿人/舆人
- 辜人
- 辟人之士
- 辦人/办人
- 辯人/辩人
- 辯護人/辩护人 (biànhùrén)
- 農人/农人 (nóngrén)
- 近人 (jìnrén)
- 迷人 (mírén)
- 送人 (sòngrén)
- 送人情
- 迷人敗本/迷人败本
- 迷人眼目
- 通事舍人
- 通人
- 逗人
- 途人 (túrén)
- 逋人
- 逢人說項/逢人说项
- 通人達才/通人达才
- 造化弄人
- 通達人情/通达人情
- 達人/达人 (dárén)
- 遊人/游人 (yóurén)
- 逼人 (bīrén)
- 道人 (dàorén)
- 過人/过人 (guòrén)
- 遇人不淑 (yùrénbùshū)
- 逼人太甚
- 過人才略/过人才略
- 達人知命/达人知命
- 過來人/过来人 (guòláirén)
- 達士通人/达士通人
- 過失殺人/过失杀人 (guòshī shārén)
- 達官貴人/达官贵人 (dáguānguìrén)
- 遊戲人間/游戏人间
- 過路人/过路人 (guòlùrén)
- 遠人/远人
- 遣人 (qiǎnrén)
- 適人/适人
- 遮人眼目
- 遮人耳目
- 選人/选人
- 遷人/迁人
- 遷客騷人/迁客骚人 (qiānkèsāorén)
- 選舉人/选举人 (xuǎnjǔrén)
- 選舉人票/选举人票
- 遽人
- 避人之處/避人之处
- 避人眼目
- 避人耳目
- 邀買人心/邀买人心 (yāomǎirénxīn)
- 邊緣人/边缘人 (biānyuánrén)
- 邊際人/边际人
- 邑人 (yìrén)
- 那起人
- 郭公真人
- 鄉下人/乡下人 (xiāngxiarén)
- 鄉人/乡人 (xiāngrén)
- 都人士
- 鄉里小人
- 鄙人 (bǐrén)
- 鄰人/邻人 (línrén)
- 鄭人爭年/郑人争年
- 鄭人買履/郑人买履 (zhèngrénmǎilǚ)
- 酒人
- 酒八仙人
- 醇酒婦人/醇酒妇人
- 醫務人員/医务人员
- 醫護人員/医护人员
- 醯人
- 里人
- 重整人
- 重新做人 (chóngxīnzuòrén)
- 野人 (yěrén)
- 野人獻曝/野人献曝
- 野人獻芹/野人献芹
- 量酒人
- 金人
- 金人緘口/金人缄口
- 金星人 (jīnxīngrén)
- 金臂人
- 金針度人/金针度人
- 針灸銅人/针灸铜人 (zhēnjiǔ tóng rén)
- 釣人/钓人
- 銅人/铜人 (tóngrén)
- 鋒芒逼人/锋芒逼人
- 錫人/锡人 (xīrén)
- 錢親人不親/钱亲人不亲
- 鍼灸銅人/针灸铜人
- 鐵人/铁人 (tiěrén)
- 鐵人三項/铁人三项 (tiěrén sān xiàng)
- 鐵石人/铁石人
- 長人/长人 (chángrén)
- 長大成人/长大成人
- 門上人/门上人
- 門人/门人 (ménrén)
- 門戶人家/门户人家
- 門裡人/门里人
- 閒人/闲人 (xiánrén)
- 閒雜人等/闲杂人等
- 閱聽人/阅听人
- 閽人/阍人 (hūnrén)
- 閹人/阉人 (yānrén)
- 闊人/阔人 (kuòrén)
- 闃其無人/阒其无人
- 關人/关人
- 關係人/关系人
- 防送人
- 防送公人
- 阿利安人
- 陌生人 (mòshēngrén)
- 陌路人 (mòlùrén)
- 陳人/陈人
- 陰人/阴人 (yīnrén)
- 陷人坑
- 陰陽人/阴阳人 (yīnyángrén)
- 階級敵人/阶级敌人
- 隸人/隶人 (lìrén)
- 雅人
- 雅人深致
- 雞人/鸡人
- 雙立人兒/双立人儿 (shuānglìrénr)
- 雙重人格/双重人格
- 難中人/难中人
- 難人/难人
- 雨人 (yǔrén)
- 雪人 (xuěrén)
- 雲水道人/云水道人
- 震撼人心 (zhènhànrénxīn)
- 靈人/灵人
- 靈魂人物/灵魂人物 (línghún rénwù)
- 非人 (fēirén)
- 非人不傳/非人不传
- 非常之人
- 非母語人士/非母语人士 (fēi-mǔyǔ rénshì)
- 非異人任/非异人任 (fēiyìrénrèn)
- 面無人色/面无人色
- 韗人/𱂈人
- 順人應天/顺人应天
- 順天應人/顺天应人
- 順水人情/顺水人情 (shùnshuǐrénqíng)
- 領袖人物/领袖人物
- 頭人/头人 (tóurén)
- 頹人/颓人
- 頭面人物/头面人物
- 額外之人/额外之人
- 類人猿/类人猿 (lèirényuán)
- 顧人/顾人
- 風人/风人
- 風俗人情/风俗人情
- 風土人情/风土人情 (fēngtǔrénqíng)
- 風流人物/风流人物
- 風雲人物/风云人物 (fēngyúnrénwù)
- 飛鳥依人/飞鸟依人
- 食人唔𦧲骨
- 食人魚/食人鱼 (shírényú)
- 食人鯊/食人鲨
- 食人鯧/食人鲳 (shírénchāng)
- 飲食之人/饮食之人
- 飽人不知餓人饑/饱人不知饿人饥
- 飽人勿知餓人饑/饱人勿知饿人饥
- 養家人/养家人
- 餐霞人
- 館人/馆人
- 饋人/馈人
- 饒人/饶人
- 首人
- 香火道人
- 香草美人
- 馬仰人翻/马仰人翻 (mǎyǎngrénfān)
- 馬來人/马来人 (Mǎláirén)
- 馬壯人強/马壮人强
- 馬雅人/马雅人
- 駕上人/驾上人
- 駭人/骇人 (hàirén)
- 駭人耳目/骇人耳目
- 駭人聽聞/骇人听闻 (hàiréntīngwén)
- 騙人/骗人 (piànrén)
- 騶人/驺人
- 騷人/骚人 (sāorén)
- 騷人墨客/骚人墨客 (sāorénmòkè)
- 驀生人/蓦生人
- 驕人/骄人 (jiāorén)
- 驚人/惊人 (jīngrén)
- 驚為天人/惊为天人 (jīngwéitiānrén)
- 高人 (gāorén)
- 高人一等 (gāorényīděng)
- 高人一籌/高人一筹
- 高人勝士/高人胜士
- 高人逸士
- 高層人士/高层人士
- 鬼怕惡人/鬼怕恶人
- 魯人/鲁人 (lǔrén)
- 魯班真人/鲁班真人
- 鮑人/鲍人
- 鮫人/鲛人
- 鮮為人知/鲜为人知 (xiǎnwéirénzhī)
- 鳥人/鸟人
- 鹵人/卤人
- 麗人/丽人 (lìrén)
- 麗人行/丽人行
- 麥丘老人/麦丘老人
- 麵人兒/面人儿 (miànrénr)
- 黃種人/黄种人 (huángzhǒngrén)
- 黎丘丈人
- 黎人
- 黏人
- 黑人 (hēirén)
- 黑人問題/黑人问题
- 黑人靈歌/黑人灵歌
- 黑人音樂/黑人音乐 (hēirén yīnyuè)
- 黑種人/黑种人 (hēizhǒngrén)
- 黨人/党人 (dǎngrén)
- 齊人/齐人 (qírén)
- 齊人之福/齐人之福
- 齊人攫金/齐人攫金
Descendants
[edit]Etymology 2
[edit]| simp. and trad. |
人 | |
|---|---|---|
| alternative forms | 儂/侬 𠆧 | |
The Min native word for “person”; used as a replacement character for 儂/侬. It is historically attested for Hokkien in the Arte de la Lengua Chiõ Chiu (1620) and Dictionario Hispanico Sinicum (1626-1642).[1][2] Use of 人 for Hokkien is recommended by Taiwan's Ministry of Education (ROC MOE).
Pronunciation 1
[edit]- Eastern Min (BUC): nè̤ng
- Southern Min
- Eastern Min
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: nè̤ng
- Sinological IPA (key): /nˡøyŋ⁵³/
- (Fuzhou)
- Southern Min
Definitions
[edit]人 (Coastal Min)
- man; person; people; human being; Homo sapiens (Classifier: 個/个 mn; 隻/只 md)
- a person associated with a particular identity or trait; -er
- 臺灣人/台湾人 [Hokkien] ― Tâi-oân-lâng [Pe̍h-ōe-jī] ― Taiwanese
- physical, psychological or moral quality or condition
Compounds
[edit]Pronunciation 2
[edit]- Eastern Min (BUC): nè̤ng
- Southern Min
- Eastern Min
- (Fuzhou)
- Bàng-uâ-cê: nè̤ng
- Sinological IPA (key): /nˡøyŋ⁵³/
- (Fuzhou)
- Southern Min
- (Hokkien: Xiamen, Zhangzhou)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: lāng
- Tâi-lô: lāng
- Phofsit Daibuun: lang
- IPA (Xiamen, Zhangzhou): /laŋ²²/
- (Hokkien: Quanzhou)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: lǎng
- Tâi-lô: lǎng
- IPA (Quanzhou): /laŋ²²/
- (Hokkien: General Taiwanese, Singapore)
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī: lâng
- Tâi-lô: lâng
- Phofsit Daibuun: laang
- IPA (Kaohsiung): /laŋ²³/
- IPA (Taipei, Singapore): /laŋ²⁴/
- (Teochew)
- Peng'im: nang7
- Pe̍h-ōe-jī-like: nāng
- Sinological IPA (key): /naŋ¹¹/
- (Hokkien: Xiamen, Zhangzhou)
Definitions
[edit]人 (Coastal Min)
Synonyms
[edit]- (Mandarin) 人家
References
[edit]- ^ Dictionario Hispánico-Sinicum[1] (overall work in Early Modern Spanish, Hokkien, and Classical Mandarin), kept as Vocabulario Español-Chino con caracteres chinos (TOMO 215) in the University of Santo Tomás Archives, Manila: Dominican Order of Preachers, 1626-1642; republished as Lee, Fabio Yuchung (李毓中), Chen, Tsung-jen (陳宗仁), José, Regalado Trota, Caño, José Luis Ortigosa, editors, Hokkien Spanish Historical Document Series I: Dictionario Hispanico Sinicum[2], Hsinchu: National Tsing Hua University Press, 2018, →ISBN
- ^ Mançano, Melchior, Feyjoó, Raymundo (1620) Arte de la Lengua Chiõ Chiu[3], Manila; Biblioteca Patrimonial Digital edition, Barcelona: Universitat de Barcelona, Centre de Recursos per a l'Aprenentatge i la Investigació, 2015
Further reading
[edit]- “人”, in 漢語多功能字庫 (Multi-function Chinese Character Database)[7], 香港中文大學 (the Chinese University of Hong Kong), 2014–
- Dictionary of Chinese Character Variants (教育部異體字字典), A00068
- “Entry #52”, in 臺灣閩南語常用詞辭典 [Dictionary of Frequently-Used Taiwan Minnan] (overall work in Mandarin and Hokkien), Ministry of Education, R.O.C., 2023.
Japanese
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]- Go-on: にん (nin, Jōyō)
- Kan-on: じん (jin, Jōyō)
- Kun: ひと (hito, 人, Jōyō); り (ri, 人)
- Nanori: きよ (kiyo); さね (sane); じ (ji); たみ (tami); と (to); ね (ne); ひこ (hiko); ひとし (hitoshi); ふと (futo); ふみ (fumi); むと (muto); め (me)
Compounds
[edit]Etymology 1
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 人 |
| ひと Grade: 1 |
| kun'yomi |
⟨pi1to2⟩ → */pʲitə/ → /fito/ → /hito/ → /çito/
From Old Japanese, from Proto-Japonic *pitə.
First attested in the Kojiki of 712 CE.[1]
Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]- a person, human
- an individual
- Synonym: 個人 (kojin)
- mankind, people
- character, personality
- an average person
- Synonym: 世人 (sejin, yohito)
- (law) legal person
- This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}. - This term needs a translation to English. Please help out and add a translation, then remove the text
{{rfdef}}. - an adult
- someone (else)
- 人の物を盗む
- hito no mono onusumu
- to steal someone's things; to steal people's things
- 人の物を盗む
Usage notes
[edit]- When scientifically referring to humans, this term is often spelled in katakana, as ヒト.
- From Old Japanese or Middle Japanese development, hito is sometimes shifted to -uto, -udo, -to, -tto, or -do.
Derived terms
[edit]- 人人 (hitobito), 人々 (hitobito, “people”)
- 人垣 (hitogaki)
- 人影 (hitokage, “figure or shadow of a person”)
- 人柄 (hitogara)
- 人気 (hitoke)
- 人心 (hitogokoro)
- 人質 (hitojichi)
- 人魂 (hitodama)
- 人伝 (hitozute)
- 人手 (hitode)
- 人出 (hitode)
- 為人 (hitotonari)
- 人並 (hitonami), 人並み (hitonami)
- 人波 (hitonami)
- 人の世 (hito no yo): this world, the world of humans (as opposed to the world of the gods)
- 人前 (hitomae)
- 人身 (hitomi)
- 商人 (akyūdo), 商人 (akindo, “trader, shopkeeper, merchant”)
- 弟 (otōto, “younger brother”)
- 首 (obito): a chief or boss; a clan in ancient Japan
- 狩人 (karyūdo), 猟人 (karyūdo)
- 玄人 (kurōto, “expert, professional”)
- 蔵人 (kurōdo)
- 恋人 (koibito)
- 妹 (imōto, “younger sister”)
- 舅 (shūto, “father-in-law”)
- 姑 (shūto, “mother-in-law”)
- 素人 (shirōto, “amateur, novice”)
- 旅人 (tabibito)
- 官人 (tsukasabito)
- 仲人 (nakōdo, “go-between, matchmaker”)
- 隼人 (hayahito), 隼人 (hayato)
- 真人 (mahito), 真人 (matōdo), 真人 (mōto): a clan in ancient Japan; a noble; someone who is very honest and straightforward
- 客人 (marōdo, “visitor, guest”)
- 召人 (meshūdo)
- 囚人 (meshūdo, “prisoner”)
- 寄人 (yoribito), 寄人 (yoryūdo)
- 若人 (wakōdo)
Pronoun
[edit]Etymology 2
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 人 |
| にん Grade: 1 |
| goon |
From Early Middle Chinese 人 (MC nyin). The goon reading, so likely the initial borrowing. Compare Shanghainese nyin.
Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]- a personality
- the role of that person
Derived terms
[edit]Counter
[edit]Affix
[edit]Etymology 3
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 人 |
| じん Grade: 1 |
| kan'on |
From Late Middle Chinese 人 (MC nyin). The kan'on reading, so likely a later borrowing. Compare Mandarin 人 (rén).
Pronunciation
[edit]Suffix
[edit]Usage notes
[edit]When compounding, makes the accent fall on the 自立拍 (jiritsuhaku, “autonomous mora”) immediately before itself. For example:
- 中国 (ちゅꜜうごく) + 人 → 中国人 (ちゅうごくꜜじん)
- アメリカ + 人 → アメリカ人 (アメリカꜜじん)
- 朝鮮 (ちょうせꜜん) + 人 → 朝鮮人 (ちょうせꜜんじん; ん is a 特殊拍 (tokushuhaku, “special mora”), therefore accentless)
- スペꜜイン + 人 → スペイン人 (スペイꜜンじん; ン is a 特殊拍 (tokushuhaku, “special mora”), therefore accentless)
- ノルウェꜜー + 人 → ノルウェー人 (ノルウェꜜーじん; ー is a 特殊拍 (tokushuhaku, “special mora”), therefore accentless)
There is one notable exception:
Derived terms
[edit]- 人影 (jin'ei)
- 人為 (jin'i)
- 人格 (jinkaku)
- 人間 (jinkan)
- 人語 (jingo)
- 人後 (jingo)
- 人権 (jinken)
- 人口 (jinkō)
- 人工 (jinkō)
- 人孔 (jinkō, “manhole”)
- 人行 (jinkō)
- 人材 (jinzai)
- 人事 (jinji)
- 人種 (jinshu)
- 人心 (jinshin)
- 人身 (jinshin)
- 人生 (jinsei)
- 人選 (jinsen)
- 人体 (jintai)
- 人道 (jindō)
- 人徳 (jintoku)
- 人物 (jinbutsu)
- 人望 (jinbō)
- 人名 (jinmei)
- 人命 (jinmei)
- 人類 (jinrui)
- 人和 (jinwa)
- 偉人 (ijin)
- 異人 (ijin)
- 歌人 (kajin)
- 家人 (kajin)
- 佳人 (kajin)
- 華人 (kajin)
- 怪人 (kaijin, “monster”)
- 外人 (gaijin)
- 官人 (kanjin)
- 漢人 (kanjin)
- 客人 (kyakujin)
- 求人 (kyūjin)
- 旧人 (kyūjin)
- 狂人 (kyōjin)
- 軍人 (gunjin, “serviceman, member of the military”)
- 吾人 (gojin)
- 後人 (kōjin)
- 公人 (kōjin)
- 工人 (kōjin)
- 詩人 (shijin)
- 私人 (shijin)
- 新人 (shinjin)
- 成人 (seijin)
- 聖人 (seijin)
- 星人 (seijin)
- 前人 (zenjin)
- 達人 (tatsujin)
- 旅人 (ryojin)
- 党人 (tōjin)
- 唐人 (tōjin)
- 俳人 (haijin)
- 廃人 (haijin)
- 閑人 (himajin), 暇人 (himajin, “man of leisure”)
- 無人 (bujin), 無人 (mujin)
- 魔人 (majin)
- 老人 (rōjin)
- 外国人 (gaikokujin, “foreigner”)
Affix
[edit]- man
- Short for 人造 (jinzō): artificial, synthetic
Etymology 4
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 人 |
| り Grade: 1 |
| irregular |
From Old Japanese. The protoform may have been -ri or -tari, see 二人 (futari, literally “two people”).
Counter
[edit]Derived terms
[edit]See also
[edit]| Japanese number-counter combinations for 人 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 一人 (hitori) 一人 (ichinin) |
二人 (futari) 二人 (ninin) |
三人 (sannin) 三人 (mitari) |
四人 (yonin) 四人 (yotari) 四人 (yottari) |
五人 (gonin) 五人 (itsutari) |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 六人 (rokunin) 六人 (mutari) 六人 (muyutari) |
七人 (shichinin) 七人 (nananin) 七人 (nanatari) |
八人 (hachinin) 八人 (yatari) |
九人 (kunin) 九人 (kyūnin) 九人 (kokonotari) |
十人 (jūnin) 十人 (totari) |
| 20 | 100 | 1,000 | 10,000 | How many? |
| 二十人 (nijūnin) 廿人 (nijūnin) 二十人 (hatatari) 廿人 (hatatari) |
百人 (hyakunin) 百人 (momotari) |
千人 (sennin) 千人 (chitari) |
一万人 (ichimannin) 万人 (mannin) 万人 (bannin) |
何人 (nannin) 幾人 (ikunin) 幾人 (ikutari) |
References
[edit]- ^ “人”, in 日本国語大辞典 [Nihon Kokugo Daijiten][4] (in Japanese), concise edition, Tokyo: Shogakukan, 2000
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 NHK Broadcasting Culture Research Institute, editor (1998), NHK日本語発音アクセント辞典 [NHK Japanese Pronunciation Accent Dictionary] (in Japanese), Tokyo: NHK Publishing, Inc., →ISBN
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kindaichi, Kyōsuke et al., editors (1997), 新明解国語辞典 [Shin Meikai Kokugo Jiten] (in Japanese), Fifth edition, Tokyo: Sanseidō, →ISBN
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Matsumura, Akira, editor (2006), 大辞林 [Daijirin] (in Japanese), Third edition, Tokyo: Sanseidō, →ISBN
Korean
[edit]Etymology
[edit]From Middle Chinese 人 (MC nyin).
| Historical Readings | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dongguk Jeongun Reading | ||
| Dongguk Jeongun, 1448 | ᅀᅵᆫ (Yale: zìn) | |
| Middle Korean | ||
| Text | Eumhun | |
| Gloss (hun) | Reading | |
| Hunmong Jahoe, 1527[8] | 사〯ᄅᆞᆷ (Yale: sǎlòm) | ᅀᅵᆫ (Yale: zìn) |
Pronunciation
[edit]- (SK Standard/Seoul) IPA(key): [in]
- Phonetic hangul: [인]
Hanja
[edit]Compounds
[edit]- 인간 (人間, in'gan)
- 인격 (人格, in'gyeok)
- 인공 (人工, in'gong)
- 인구 (人口, in'gu)
- 인기 (人氣, in'gi)
- 인도 (人道, indo)
- 인력 (人力, illyeok)
- 인류 (人類, illyu)
- 인망 (人望, inmang)
- 인명 (人名, inmyeong)
- 인문 (人文, inmun)
- 인물 (人物, inmul)
- 인민 (人民, inmin)
- 인분 (人分, inbun)
- 인사 (人事, insa)
- 인사 (人士, insa)
- 인삼 (人蔘, insam, “ginseng”)
- 인상 (人相, insang)
- 인생 (人生, insaeng)
- 인성 (人性, inseong)
- 인어 (人魚, ineo)
- 인원 (人員, inwon)
- 인재 (人材, injae)
- 인정 (人情, injeong)
- 인종 (人種, injong)
- 인체 (人體, inche)
- 인형 (人形, inhyeong)
- 인화 (人和, inhwa)
- 가인 (佳人, gain)
- 가인 (家人, gain)
- 개인 (個人, gaein)
- 거인 (巨人, geoin)
- 걸인 (乞人, georin)
- 고인 (古人, goin)
- 고인 (故人, goin)
- 광인 (狂人, gwang'in)
- 교인 (敎人, gyoin)
- 군인 (軍人, gunin)
- 궁인 (宮人, gung'in)
- 귀인 (貴人, gwiin)
- 나인 (內人, nain)
- 낭인/랑인 (浪人, nang'in/rang'in)
- 노인/로인 (老人, noin/roin)
- 달인 (達人, darin)
- 당인 (黨人, dang'in)
- 대인 (大人, daein)
- 명인 (名人, myeong'in)
- 무인 (武人, mu'in)
- 미인 (美人, miin)
- 백인 (白人, baegin)
- 범인 (犯人, beomin)
- 법인 (法人, beobin)
- 본인 (本人, bonin)
- 부인 (夫人, bu'in)
- 부인 (婦人, bu'in)
- 살인 (殺人, sarin)
- 상인 (商人, sang'in)
- 설인 (雪人, seorin)
- 성인 (成人, seong'in)
- 성인 (聖人, seong'in)
- 속인 (俗人, sogin)
- 시인 (詩人, siin)
- 신인 (新人, sinin)
- 악인 (惡人, agin)
- 애인 (愛人, aein)
- 야인 (野人, yain)
- 양인/량인 (良人, yang'in/ryang'in)
- 여인 (女人, yeoin)
- 연인/련인 (戀人, yeonin/ryeonin)
- 왜인 (倭人, waein)
- 외인 (外人, oein)
- 우인 (偶人, u'in)
- 우인 (愚人, u'in)
- 위인 (偉人, wiin)
- 은인 (恩人, eunin)
- 의인 (義人, uiin)
- 이인 (異人, iin)
- 장인 (丈人, jang'in)
- 죄인 (罪人, joein)
- 주인 (主人, ju'in)
- 증인 (證人, jeung'in)
- 철인 (哲人, cheorin)
- 철인 (鐵人, cheorin)
- 초인 (超人, choin)
- 토인 (土人, toin)
- 폐인 (廢人, pyein)
- 현인 (賢人, hyeonin)
- 흑인 (黑人, heugin)
- 인격화 (人格化, in'gyeokhwa)
- 인력거 (人力車, illyeokgeo)
- 인류학 (人類學, illyuhak)
- 인민폐 (人民幣, inminpye)
- 인삼차 (人蔘茶, insamcha)
- 인형극 (人形劇, inhyeonggeuk)
- 노인학/로인학 (老人學, noinhak/roinhak)
- 살인자 (殺人者, sarinja)
- 선인장 (仙人掌, seoninjang)
- 유인원 (類人猿, yuinwon)
- 주인공 (主人公, ju'in'gong)
- 고소인 (告訴人, gosoin)
- 관리인 (管理人, gwalliin)
- 기업인 (企業人, gieobin)
- 대리인 (代理人, daeriin)
- 미망인 (未亡人, mimang'in)
- 보증인 (保證人, bojeung'in)
- 서양인 (西洋人, seoyang'in)
- 야만인 (野蠻人, yamanin)
- 언론인 (言論人, eollonin)
- 연예인 (演藝人, yeonyein)
- 외계인 (外界人, oegyein)
- 외국인 (外國人, oegugin)
- 우주인 (宇宙人, uju'in)
- 유태인 (猶太人, yutaein)
- 일반인 (一般人, ilbanin)
- 일본인 (日本人, ilbonin)
- 장애인 (障礙人/障碍人, jang'aein)
- 정치인 (政治人, jeongchiin)
- 조선인 (朝鮮人, joseonin)
- 죽부인 (竹夫人, jukbu'in)
- 중국인 (中國人, junggugin)
- 중재인 (仲裁人, jungjaein)
- 지구인 (地球人, jigu'in)
- 지배인 (支配人, jibaein)
- 지식인 (知識人, jisigin)
- 한국인 (韓國人, han'gugin)
- 현대인 (現代人, hyeondaein)
- 후견인 (後見人, hugyeonin)
- 인면수심 (人面獸心, inmyeonsusim)
- 인본주의 (人本主義, inbonjuui)
- 인산인해 (人山人海, insaninhae)
- 인신공격 (人身攻擊, insin'gonggyeok)
- 민주당원 (民主黨人, minjudang'won)
References
[edit]- 국제퇴계학회 대구경북지부 (國際退溪學會 大邱慶北支部) (2007). Digital Hanja Dictionary, 전자사전/電子字典. [9]
Kunigami
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]人 (chū)
Miyako
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]人 (psïtu)
Okinawan
[edit]Kanji
[edit]Readings
[edit]Compounds
[edit]- 人間 (ninjin)
Etymology 1
[edit]| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 人 |
| っちゅ Grade: 1 |
| kun'yomi |
Pronunciation
[edit]Noun
[edit]人 (tchu)
Derived terms
[edit]- 沖縄ん人 (uchinānchu): Okinawans, Okinawa people
- 八重山ん人 (yēyamanchu): Yaeyamans, Yaeyama people
- 大人 (ufutchu): adult
- 海人 (nminchu)
Etymology 2
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Noun
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Derived terms
[edit]- The time allocated for running scripts has expired.: Yaeyamans, Yaeyama people
Etymology 3
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Noun
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Derived terms
[edit]- The time allocated for running scripts has expired.: public servant, civil servant, government official
Counter
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
- The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Derived terms
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Etymology 4
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Counter
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
- The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Derived terms
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Etymology 5
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Counter
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
- The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Derived terms
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Vietnamese
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Han character
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
- The time allocated for running scripts has expired. The time allocated for running scripts has expired. form of The time allocated for running scripts has expired..
- The time allocated for running scripts has expired. The time allocated for running scripts has expired. form of The time allocated for running scripts has expired..
Compounds
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
References
[edit]
Yaeyama
[edit]Kanji
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Readings
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Pronunciation
[edit]- The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Noun
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Yonaguni
[edit]Kanji
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Readings
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Pronunciation
[edit]- The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
Noun
[edit]The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
The time allocated for running scripts has expired.
- Character boxes with images
- CJK Unified Ideographs block
- Han script characters
- Kangxi Radicals block
- Han character radicals
- Translingual lemmas
- Translingual symbols
- CJKV radicals
- Han pictograms
- Chinese terms inherited from Proto-Sino-Tibetan
- Chinese terms derived from Proto-Sino-Tibetan
- Mandarin terms with audio links
- Chinese lemmas
- Mandarin lemmas
- Sichuanese lemmas
- Dungan lemmas
- Cantonese lemmas
- Taishanese lemmas
- Gan lemmas
- Hakka lemmas
- Jin lemmas
- Northern Min lemmas
- Eastern Min lemmas
- Hokkien lemmas
- Teochew lemmas
- Wu lemmas
- Xiang lemmas
- Middle Chinese lemmas
- Old Chinese lemmas
- Chinese hanzi
- Mandarin hanzi
- Sichuanese hanzi
- Dungan hanzi
- Cantonese hanzi
- Taishanese hanzi
- Gan hanzi
- Hakka hanzi
- Jin hanzi
- Northern Min hanzi
- Eastern Min hanzi
- Hokkien hanzi
- Teochew hanzi
- Wu hanzi
- Xiang hanzi
- Middle Chinese hanzi
- Old Chinese hanzi
- Chinese nouns
- Mandarin nouns
- Sichuanese nouns
- Dungan nouns
- Cantonese nouns
- Taishanese nouns
- Gan nouns
- Hakka nouns
- Jin nouns
- Northern Min nouns
- Eastern Min nouns
- Hokkien nouns
- Teochew nouns
- Wu nouns
- Xiang nouns
- Middle Chinese nouns
- Old Chinese nouns
- Chinese adjectives
- Mandarin adjectives
- Sichuanese adjectives
- Dungan adjectives
- Cantonese adjectives
- Taishanese adjectives
- Gan adjectives
- Hakka adjectives
- Jin adjectives
- Northern Min adjectives
- Eastern Min adjectives
- Hokkien adjectives
- Teochew adjectives
- Wu adjectives
- Xiang adjectives
- Middle Chinese adjectives
- Old Chinese adjectives
- Chinese pronouns
- Mandarin pronouns
- Chinese proper nouns
- Mandarin proper nouns
- Sichuanese proper nouns
- Dungan proper nouns
- Cantonese proper nouns
- Taishanese proper nouns
- Gan proper nouns
- Hakka proper nouns
- Jin proper nouns
- Northern Min proper nouns
- Eastern Min proper nouns
- Hokkien proper nouns
- Teochew proper nouns
- Wu proper nouns
- Xiang proper nouns
- Middle Chinese proper nouns
- Old Chinese proper nouns
- Chinese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Chinese terms spelled with 人
- Chinese nouns classified by 個/个
- Chinese nouns classified by 隻/只
- Mandarin terms with collocations
- Mandarin terms with usage examples
- Cantonese terms with usage examples
- Hokkien terms with quotations
- Cantonese terms with collocations
- Literary Chinese terms with quotations
- Chinese nouns classified by 份
- Chinese terms with obsolete senses
- zh:Fantasy
- zh:Mythology
- Cantonese Chinese
- Zhao'an Hakka
- Hakka terms with collocations
- Beijing Mandarin
- Taishanese Chinese
- Chinese surnames
- Hokkien terms with audio links
- Hokkien terms with collocations
- Hokkien terms with usage examples
- Eastern Min pronouns
- Hokkien pronouns
- Teochew pronouns
- Beginning Mandarin
- zh:Hominids
- zh:People
- Japanese kanji
- Japanese first grade kanji
- Japanese kyōiku kanji
- Japanese jōyō kanji
- Japanese kanji with goon reading にん
- Japanese kanji with kan'on reading じん
- Japanese kanji with kun reading ひと
- Japanese kanji with kun reading り
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading きよ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading さね
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading じ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading たみ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading と
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ね
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ひこ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ひとし
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ふと
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading ふみ
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading むと
- Japanese kanji with nanori reading め
- Japanese terms spelled with 人 read as ひと
- Japanese terms read with kun'yomi
- Japanese terms inherited from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms derived from Old Japanese
- Japanese terms inherited from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms derived from Proto-Japonic
- Japanese terms with IPA pronunciation
- Japanese lemmas
- Japanese nouns
- Japanese terms with multiple readings
- Japanese terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Japanese terms with 1 kanji
- Japanese terms spelled with 人
- Japanese single-kanji terms
- ja:Law
- Japanese terms with usage examples
- Japanese pronouns
- Japanese terms with archaic senses
- Japanese terms spelled with 人 read as にん
- Japanese terms read with goon
- Japanese terms derived from Early Middle Chinese
- Japanese counters
- Japanese affixes
- Japanese terms spelled with 人 read as じん
- Japanese terms read with kan'on
- Japanese terms derived from Late Middle Chinese
- Japanese suffixes
- Japanese short forms
- Japanese terms read with irregular kanji readings
- ja:People
- ja:Hominids
- Korean terms derived from Middle Chinese
- Korean lemmas
- Korean hanja
- Korean hanja forms
- Kunigami kanji
- Kunigami first grade kanji
- Kunigami kyōiku kanji
- Kunigami jōyō kanji
- Kunigami kanji with kun reading ちゅー
- Kunigami terms with IPA pronunciation
- Kunigami lemmas
- Kunigami nouns
- Kunigami terms with multiple readings
- Kunigami terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Kunigami terms with 1 kanji
- Kunigami terms spelled with 人
- Kunigami single-kanji terms
- xug:Hominids
- xug:People
- Miyako kanji
- Miyako first grade kanji
- Miyako kyōiku kanji
- Miyako jōyō kanji
- Miyako kanji with kun reading ぴぃとぅ
- Miyako terms with IPA pronunciation
- Miyako lemmas
- Miyako nouns
- Miyako terms with multiple readings
- Miyako terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Miyako terms with 1 kanji
- Miyako terms spelled with 人
- Miyako single-kanji terms
- mvi:Hominids
- mvi:People
- Okinawan kanji
- Okinawan first grade kanji
- Okinawan kyōiku kanji
- Okinawan jōyō kanji
- Okinawan kanji with on reading にん
- Okinawan kanji with kun reading っちゅ
- Okinawan kanji with kun reading ぴとぅ
- Okinawan kanji with kun reading い
- Okinawan kanji with kun reading たい
- Okinawan terms spelled with 人 read as っちゅ
- Okinawan terms read with kun'yomi
- Okinawan terms with IPA pronunciation
- Okinawan lemmas
- Okinawan nouns
- Okinawan terms with multiple readings
- Okinawan terms spelled with first grade kanji
- Okinawan terms with 1 kanji
- Okinawan terms spelled with 人
- Okinawan single-kanji terms
- Vietnamese Chữ Hán